Cinnamon Leaf EO
Naturelle
Spicy > Warm Spices > Eugenolic > Cinnamic

Crédits photo: ScenTree SAS
Latin name :
Cinnamomum zeylanicum eugenoliferum
Botanical profile :
The cinnamon tree is a tree of the Lauraceae family and the Cinnamomum genus.
Geographic origin :
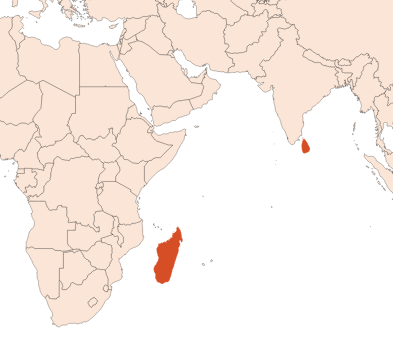
The cinnamon tree grows at low altitudes in parts of Sri Lanka, Madagascar, China and Japan
Chemotypes :
There are more than 250 species of cinnamon trees throughout Southeast Asia, China and Australia. The perfume industry generally uses only two of those varieties of cinnamon:
Cinnamomum zeylanicum : Ceylon cinnamon EO. Leaves are extracted.
Cinnamomum cassia : Chinese cinnamon or Cassia EO. Leaves from this tree are not extracted for perfumery.
We can also distinguish Cinnamomum burmanni : Korintje cassia SFE and Cinnamomum tamala : Indian cinnamon, much less cultivated.
The difference between the two types of cinnamon lies in the way they are dried. Cassia dries forming two spirals, whereas Ceylon cinnamon forms thin layers of wood which crumble easily. The chinese variety is also darker and harder. Ceylon cinnamon has a more zesty and terpenic smell than the Chinese cinnamon, which contains more Cinnamaldehyde.
Cinnamomum zeylanicum : Ceylon cinnamon EO. Leaves are extracted.
Cinnamomum cassia : Chinese cinnamon or Cassia EO. Leaves from this tree are not extracted for perfumery.
We can also distinguish Cinnamomum burmanni : Korintje cassia SFE and Cinnamomum tamala : Indian cinnamon, much less cultivated.
The difference between the two types of cinnamon lies in the way they are dried. Cassia dries forming two spirals, whereas Ceylon cinnamon forms thin layers of wood which crumble easily. The chinese variety is also darker and harder. Ceylon cinnamon has a more zesty and terpenic smell than the Chinese cinnamon, which contains more Cinnamaldehyde.
Extraction process :
The cinnamon tree is up to seven meters tall. Several parts of this tree can be extracted to obtain essential oils. When dried, the bark gives the commonly used cinnamon sticks and the leaves measures seven to eighteen centimetres long.
The leaves and the bark are mature 12 to 18 months after the preceding harvest. From red to dark green, the colour of the leaves indicates the cinnamon maturity. The culture often takes place in May and November. The leaves are collected by cutting the twigs off the tree and separating the leaves from the branches. The leaves are ground and dried before they are extracted by steam distillation.
About 1 hectare of cinnamon forest allows to cultivate 1 ton of leaves, offering a yield of 2.5 to 3 kg of essential oil (extraction yield: 0.3%).
The leaves and the bark are mature 12 to 18 months after the preceding harvest. From red to dark green, the colour of the leaves indicates the cinnamon maturity. The culture often takes place in May and November. The leaves are collected by cutting the twigs off the tree and separating the leaves from the branches. The leaves are ground and dried before they are extracted by steam distillation.
About 1 hectare of cinnamon forest allows to cultivate 1 ton of leaves, offering a yield of 2.5 to 3 kg of essential oil (extraction yield: 0.3%).
Major Components :
Eugenol (70-80%)
Benzyl Benzoate (≈4%)
Cinnamyl Acetate (≈2%)
Cinnamic Aldehyde (≈2%)
Eugenyl Acetate (≈1%)
Safrole (≈1%)
Benzyl Benzoate (≈4%)
Cinnamyl Acetate (≈2%)
Cinnamic Aldehyde (≈2%)
Eugenyl Acetate (≈1%)
Safrole (≈1%)
- Uses in perfumery :
- Useful in spicy notes and as a modifier in amber perfumes.
- Other comments :
- The smell of the leaf is different from the bark as it is closer to clove (high rate of Eugenol) than cinnamon.
Its essential oil is one of the precursors of the extraction of natural Eugenol, which can be used for the synthesis of Vanillin.
The essential oil of cinnamon leaf is less expensive than the cinnamon bark one.
Cinnamon roots can also be extracted. Their essential oil is more camphorated, earthy and floral. - Volatility :
- Heart/Base
- Appearance :
- Colorless liquid
- Stability :
- Aromatic compounds can be chromophoric and cause a coloration of the oil, especially in alkaline bases
- Price Range :
- €€
- Aromatherapy :
Informations provided below are taken from reference works in aromatherapy. They are given for information purposes only and can not constitute medical information, nor engage the responsibility of ScenTree.
The cinnamon leaf has several aromatherapic virtues: it is anti-infectious, anti-fungal, antiviral and can stimulate digestion and the immune system.
Crédits photo: ScenTree SAS
- EINECS number :
- 84649-98-9
- FEMA number :
- 2292
- Allergens :
- Cinnamaldehyde - Cinnamyl Alcohol - Eugenol - Linalool
- IFRA :
- This ingredient is restricted by IFRA
- Annexe I :
- Some regulated synthetic ingredients are found in nature and in certain proportions in natural ingredients. This presence in nature has to be taken into account when calculating limits of use recommended by the IFRA. In case you do not know these concentrations, you can use the ones estimated by the IFRA. Here they are :
- Annexe I :
- Some regulated synthetic ingredients are found in nature and in certain proportions in natural ingredients. This presence in nature has to be taken into account when calculating limits of use recommended by the IFRA. In case you do not know these concentrations, you can use the ones estimated by the IFRA. Here they are :
| List of regulated compounds contained in this ingredient | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regulated ingredient name | CAS N° | Estimated Concentration |
| Benzyl alcohol | 100-51-6 | 0,1 |
| Benzaldehyde | 100-52-7 | 0,16 |
| Cinnamyl acetate | 103-54-8 | 1,7 |
| Benzyl benzoate | 120-51-4 | 3,5 |
| Farnesol | 4602-84-0 | 0,12 |
| Coumarin | 91-64-5 | 0,3 |
| Methyl eugenol | 93-15-2 | 0,01 |
| Safrole | 94-59-7 | 1,2 |
| Eugenol | 97-53-0 | 74 |
| Isoeugenol | 97-54-1 | 0,13 |
| List of regulated compounds contained in this ingredient | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regulated ingredient name | CAS N° | Estimated Concentration |
| Benzyl alcohol | 100-51-6 | 0,1 |
| Benzaldehyde | 100-52-7 | 0,16 |
| Cinnamyl acetate | 103-54-8 | 1,7 |
| Benzyl benzoate | 120-51-4 | 3,5 |
| Farnesol | 4602-84-0 | 0,12 |
| Coumarin | 91-64-5 | 0,3 |
| Methyl eugenol | 93-15-2 | 0,01 |
| Safrole | 94-59-7 | 1,2 |
| Eugenol | 97-53-0 | 74 |
| Isoeugenol | 97-54-1 | 0,13 |
To learn more about IFRA's standards : https://ifrafragrance.org/safe-use/library
ScenTree is solely responsible for the information provided here.




