Citronellal
Naturelle - Synthétique
Citrus > Citric > Green > Zesty
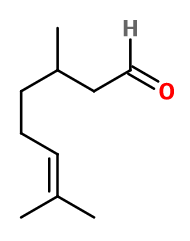
Crédits photo: ScenTree SAS
Other names :
3,7-dimethyloct-6-enal ; Dihydrocitral ; 3,7-dimethyloct-6-en-1-al ; Rhodinal
Volatility :
Head/Heart
Uses in perfumery :
Citronellal is used in lemon and lemongrass reproductions and for a citral and fresh effect in citrus notes. Can be used in rosy notes.
Natural availability :
The essential oils most commonly used to collect Citronellal in its natural state are Lemongrass EO (up to 45%) or Eucalyptus citriodora (up to 80%). The addition of bisulfite salts improves the purity of the extraction.
Year of discovery :
Discovered in 1889.
Other comments :
Citronellal is one of the 26 allergens in perfumery.
Price Range :
€€
Stability :
Aldehydes may form diethylacetals in alcoholic perfumes, with no real impact on their smell.
Terpenes tend to polymerize by oxydation.
Terpenes tend to polymerize by oxydation.

Crédits photo: ScenTree SAS
- Molecular formula :
- C10H18O
- Molecular Weight :
- 154,25 g/mol
- Density :
- 0,857
- Flash Point :
- 86°C
- Fusion Point :
- Donnée indisponible.
- Appearance :
- Colorless liquid
- Log P :
- 3,62
- Boiling Point :
- 207°C
- Detection Threshold :
- Entre 31 et 100 ppb (0,00001%) selon les personnes,
Synthesis route :
The synthesis of citronellal is made in several possible ways. The first is from Geraniol and Nerol: a rearrangement of these molecules in the presence of a catalyst that contains oxides of copper, chromium and barium allows to obtain Citronellal as final product. Citronellol, dehydrogenated under reduced pressure, in the presence of a bichromated copper steel catalyst, also allows to obtain Citronellal. The third possibility is a Citral hydrogenation catalysed by palladium.
Synthesis precursor :
Citronellal is a precursor to the synthesis of many other perfume compounds. Depending on the catalyst, its hydrogenation enables the obtention of Citronellol, dihydrocitronellal or dihydrocitronellol. An acid hydrolysis allows to synthesize Hydroxycitronellal. Cyclizing the molecule by acid catalysis also allows to obtain Pulegol, a precursor for the synthesis of L-Menthol. Finally, Citronellal forms a Schiff base by reaction with Methyl Anthranilate or Indole for example.
Isomerism :
Citronellal has an asymmetric carbon that gives rise to two enantiomers. Both isomers have a rather similar smell, although they are not necessarily present in the same plants. Usually, it is the racemic mixture of the two isomers that is used in perfumery.
Eucalyptol, Geraniol and Linalool are examples of constitutional isomers of Citronellal. Their smell is however very different, as it is more floral and camphorated for Eucalyptol.
- EINECS number :
- 203-376-6
- FEMA number :
- 2307
- JECFA number :
- 1220
- FLAVIS number :
- 05.021
- Allergens :
- Citronellal may provoke an allergic reaction on skin contact (redness, heat, scraching, prickling) for some people.
- IFRA :
- This ingredient is restricted by IFRA
- Restriction type :
- RESTRICTION
- Cause of restriction :
- DERMAL SENSITIZATION AND SYSTEMIC TOXICITY
- Amendment :
- 49
- Quantitative limit on the use :
-
Cat.1 Cat.2 Cat.3 Cat.4 Cat.5A Cat.5B Cat.5C Cat.5D Cat.6 0,41 % 0,16 % 0,026 % 0,49 % 0,33 % 0,051 % 0,1 % 0,017 % 0,82 % Cat.7A Cat.7B Cat.8 Cat.9 Cat.10A Cat.10B Cat.11A Cat.11B Cat.12 0,077 % 0,077 % 0,017 % 1,4 % 1,4 % 2,3 % 0,017 % 0,017 % No Restriction
This ingredient is not restricted for the 48th amendment
To learn more about IFRA's standards : https://ifrafragrance.org/safe-use/library
ScenTree is solely responsible for the information provided here.



