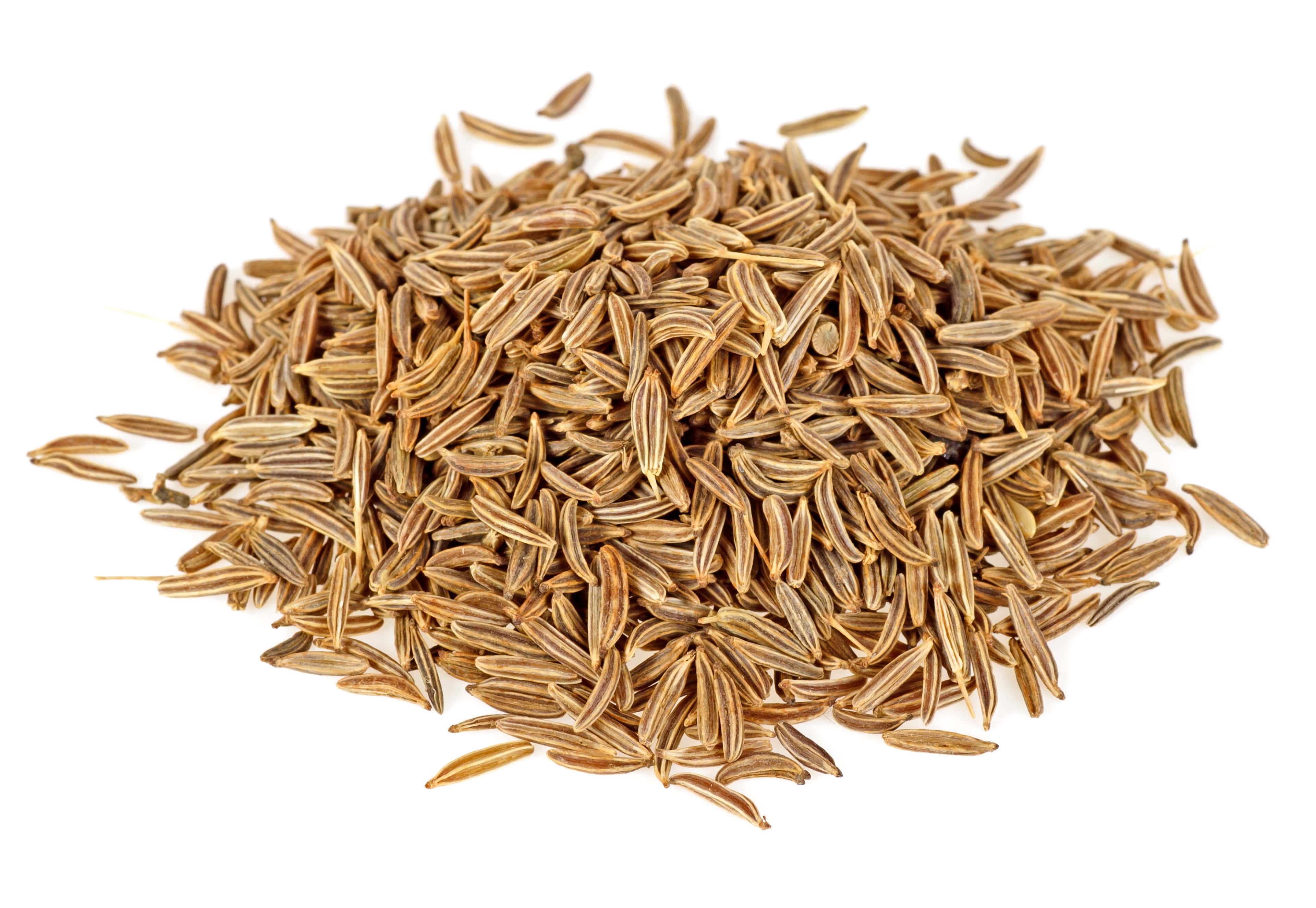
Cumin EO
Naturelle
Spicy > Warm Spices > Dry Woods > Anisic

Crédits photo: ScenTree SAS
Latin name :
Cuminum cyminum
Botanical profile :
Cumin is a plant of the Apiaceae family and the genus Cuminum.
Geographic origin :
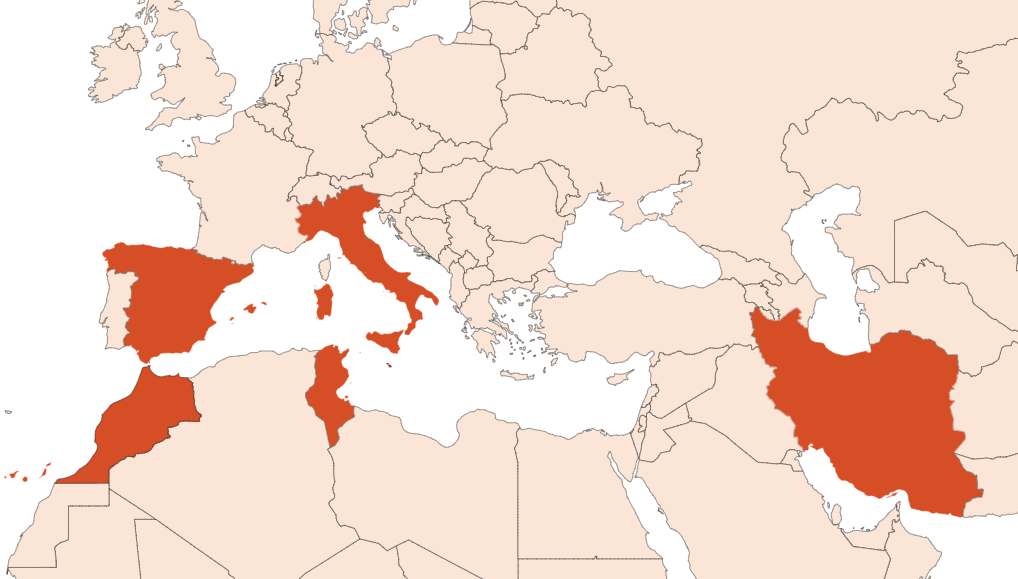
Cumin has historically originated in Egypt, Iran and India. Today the main producers are located in the Mediterranean region such as Spain, Malta, Sicily, Tunisia, Morocco and Iran.
Chemotypes :
In addition to Cuminum cyminum, which is true cumin, there is a very little cultivated variety called Cuminum setifolium.
Caraway EO is considered to be a ''false cumin '', as evidenced by the appearance of its seeds.
Caraway EO is considered to be a ''false cumin '', as evidenced by the appearance of its seeds.
Extraction process :
Cumin grows in a warm and sunny climate on a well-drained soil.
The planting of cumin is done in early spring (April), flowering in summer and the harvest is done in early autumn. At maturity, the fruits of the plant become dry, brown and had a particular scent. Inside, the egg-shaped seed is collected and used for perfumery.
The seed is dried and extracted by steaming. At the end of the process, the essential oil is collected in a essencier by decantation with a yield of about 3%.
The planting of cumin is done in early spring (April), flowering in summer and the harvest is done in early autumn. At maturity, the fruits of the plant become dry, brown and had a particular scent. Inside, the egg-shaped seed is collected and used for perfumery.
The seed is dried and extracted by steaming. At the end of the process, the essential oil is collected in a essencier by decantation with a yield of about 3%.
Major Components :
Cuminaldehyde (20-30%)
Gamma-Terpinene (15-20%)
p-Mentha-1,4-dien-7-al (15-20%)
Alpha-Pinene (13-15%)
p-Mentha-1,3-dien-7-al (≈6%)
D-Limonene (7-10%)
Para-Cymene (15%)
Gamma-Terpinene (15-20%)
p-Mentha-1,4-dien-7-al (15-20%)
Alpha-Pinene (13-15%)
p-Mentha-1,3-dien-7-al (≈6%)
D-Limonene (7-10%)
Para-Cymene (15%)
- Uses in perfumery :
- Used in woody, spicy, fougere and leather notes for a sensual effect. Mixed with oriental and floral-powdery notes for women's perfumes.
- Other comments :
- Although generally called ''seed '', the cumin part that is used is actually a fruit. Actually, this part of the plant is composed of the seed and its pericarp.
In Iran, it is possible to observe a production of cumin water, obtained by distillation of crushed fruits.
The essential oil of cumin is the main source of natural Cuminaldehyde, precursor in the synthesis of Mayol®, with the smell of lily of the valley. The content of aromatic aldehydes is one of the quality markers of the EO which must be between 40 and 52%. This ingredient is often confused with caraway because of their great visual similarities.
Cumin is the main curry spice, accompanied by ginger, coriander, cinnamon, pepper, fenugreek, bay, black pepper, cardamom, clove, mustard seeds and nutmeg. - Volatility :
- Heart
- Appearance :
- Pale yellow liquid
- Stability :
- Cuminaldehyde can form diethylacetals in stability tests, without modifying the raw material’s smell
The terpenes identified in this raw material can polymerize when they are oxidized - Price Range :
- €€€
- Aromatherapy :
Informations provided below are taken from reference works in aromatherapy. They are given for information purposes only and can not constitute medical information, nor engage the responsibility of ScenTree.
Cumin has calming (narcotic), anti-inflammatory and carminative properties (helps evacuate intestinal gas). It is recommended in cases of epigastralgia (pain in the upper abdomen), insomnia and hyperthyroidism (overproduction of hormones).
Crédits photo: ScenTree SAS
- EINECS number :
- 84775-51-9
- FEMA number :
- 2343
- Allergens :
- D-Limonene
- IFRA :
- This ingredient is restricted by IFRA
- Restriction type :
- RESTRICTION
- Cause of restriction :
- PHOTOTOXICITY
- Amendment :
- 49
- Comments :
- The Standard is set due to the phototoxic effects of Cumin oil. For more detailed information on the application of this Standard, please refer to the note on phototoxic ingredients in chapter 1 of the Guidance for the use of IFRA Standards. If the level of furocoumarins is unknown, the restriction level specified in this IFRA Standard applies. Combination effects of phototoxic ingredients are only taken into consideration for the furocoumarin-containing fragrance ingredients (extracts) listed in the IFRA Standard of Citrus oils and other furocoumarins containing essential oils. If combinations of furocoumarin-containing phototoxic fragrance ingredients (extracts) are used, the use levels must be reduced accordingly. The sum of the concentrations of all furocoumarin-containing phototoxic fragrance ingredients (extracts), expressed in of their recommended upper concentration level in the consumer product shall not exceed 100.
- Quantitative limit on the use :
-
Cat.1 Cat.2 Cat.3 Cat.4 Cat.5A Cat.5B Cat.5C Cat.5D Cat.6 0,4 % 0,4 % 0,4 % 0,4 % 0,4 % 0,4 % 0,4 % 0,4 % 0,4 % Cat.7A Cat.7B Cat.8 Cat.9 Cat.10A Cat.10B Cat.11A Cat.11B Cat.12 No Restriction 0,4 % 0,4 % No Restriction No Restriction 0,4 % No Restriction 0,4 % No Restriction - Annexe I :
- Some regulated synthetic ingredients are found in nature and in certain proportions in natural ingredients. This presence in nature has to be taken into account when calculating limits of use recommended by the IFRA. In case you do not know these concentrations, you can use the ones estimated by the IFRA. Here they are :
- Restriction type :
- RESTRICTION NON QRA
- Cause of restriction :
- PHOTOTOXICITY
- Amendment :
- 48
- Comments :
- The limit only applies to applications on skin exposed to sunshine, excluding rinse-off products (please refer to Table 4 of the QRA booklet for more detailed information). If combinations of phototoxic fragrance ingredients are used, the use levels have to be reduced accordingly. The sum of the concentrations of all phototoxic ingredients, expressed in % of their recommended maximum level in the consumer product shall not exceed 100. Note: See remark on phototoxic ingredients in the Introduction to the IFRA Standards (Appendix 8 to the IFRA Code of Practice) and the Standard on Citrus oil and other furocoumarins-containing essential oils.
- Annexe I :
- Some regulated synthetic ingredients are found in nature and in certain proportions in natural ingredients. This presence in nature has to be taken into account when calculating limits of use recommended by the IFRA. In case you do not know these concentrations, you can use the ones estimated by the IFRA. Here they are :
| List of regulated compounds contained in this ingredient | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regulated ingredient name | CAS N° | Estimated Concentration |
| Cuminaldehyde | 122-03-2 | 21 |
| p-Isopropylbenzyl alcohol | 536-60-7 | 0,2 |
| Skin contact products | Non skin contact products | |
|---|---|---|
| Leave on products | Rinse off products | |
| 0,4 % | X | X |
| List of regulated compounds contained in this ingredient | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regulated ingredient name | CAS N° | Estimated Concentration |
| Cuminaldehyde | 122-03-2 | 21 |
| p-Isopropylbenzyl alcohol | 536-60-7 | 0,2 |
To learn more about IFRA's standards : https://ifrafragrance.org/safe-use/library
ScenTree is solely responsible for the information provided here.


