Lemon EO
Naturelle
Citrus > Zesty > Citric

Crédits photo: ScenTree SAS
Latin name :
Citrus limon
Botanical profile :
The lemon tree is a tree of the Rutaceae family and the Citrus genus.
Geographic origin :
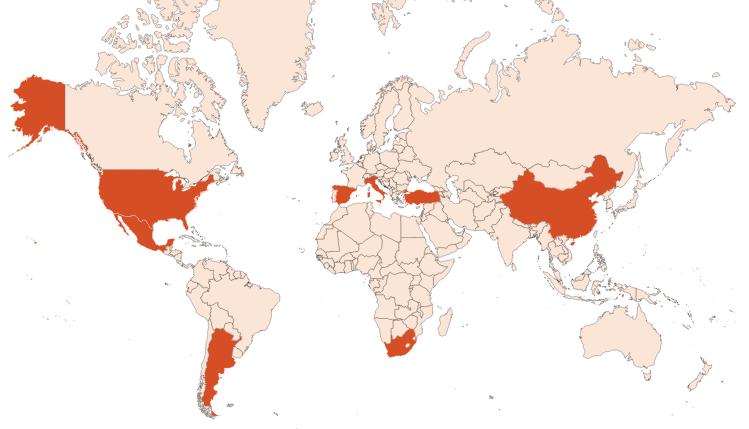
Lemon trees can be found in tropical and subtropical regions of the world but it is mainly cultivated in the USA (California or Florida) as well as around the Mediterranean sea. Sicilian production accounts for more than half of world production. There are also productions in Argentina, Spain, Turkey, China, South Africa and Mexico
Chemotypes :
The genus Citrus includes the vast majority of citrus fruits and includes a large number of varieties available in perfumery:
Bergamot - (Citrus bergamia) is a hybrid of lemon and bitter orange, grown for the essential oil of its fruit and petitgrain.
Bitter orange or bigarade orange - (Citrus aurantium), grown in Spain and Florida.
Citron - (Citrus medica), grown in Italy (Sicily).
Lemon - (Citrus limon), cultured in Italy for the essential oil of its fruit and of its leafy twigs (Petitgrain).
Combava - (Citrus hystrix), grown in Thailand and India.
Lime - (Citrus aurantifolia), grown for its fruit in Mexico for the most part.
Mandarin - (Citrus reticulata), grown mainly in Italy for its fruit and for its petitgrain, by extracting the leaves from the tree. Its hybrid with sweet orange gave birth to clementine.
Orange - (Citrus sinensis) is famous for the cultivation of its fruits, whose juice and essential oil are extracted in Brazil and California in particular, which is the most used of all perfumes.
Grapefruit - (Citrus paradisii) of Malay origin, is cultivated for its essential oil in Brazil and Israel in particular.
Yuzu - (Citrus junos), produced in Japan and Korea.
Bergamot - (Citrus bergamia) is a hybrid of lemon and bitter orange, grown for the essential oil of its fruit and petitgrain.
Bitter orange or bigarade orange - (Citrus aurantium), grown in Spain and Florida.
Citron - (Citrus medica), grown in Italy (Sicily).
Lemon - (Citrus limon), cultured in Italy for the essential oil of its fruit and of its leafy twigs (Petitgrain).
Combava - (Citrus hystrix), grown in Thailand and India.
Lime - (Citrus aurantifolia), grown for its fruit in Mexico for the most part.
Mandarin - (Citrus reticulata), grown mainly in Italy for its fruit and for its petitgrain, by extracting the leaves from the tree. Its hybrid with sweet orange gave birth to clementine.
Orange - (Citrus sinensis) is famous for the cultivation of its fruits, whose juice and essential oil are extracted in Brazil and California in particular, which is the most used of all perfumes.
Grapefruit - (Citrus paradisii) of Malay origin, is cultivated for its essential oil in Brazil and Israel in particular.
Yuzu - (Citrus junos), produced in Japan and Korea.
Extraction process :
Lemon is the fruit of the lemon tree, a thorny tree that is 3 to 8 meters tall with evergreen leaves and white flowers.
The harvest usually takes place between the months of November and May, although it is possible to obtain fruit all year round. The fruits are harvested mechanically before they are washed and sent to a sfumatrice. The machine breaks the zest to collect the essential oil. This oil is driven to a centrifuge by a stream of water and centrifuged twice after the filtration of the residual zest. The zest is collected to be steam distilled during 4 hours. Thus, one oil is obtained by cold press, and another by steaming.
The extraction yield of lemon zest is between 0.3 and 0.5%.
It is also possible to perform a less common hydrodistillation, starting from the fresh peel. For this method, the fruit passes directly into a peeling machine to separate the zest from the pulp and extract the fruit peel only.
The essential oil can be deterpened or desesquiterpened, to increase the intensity (a deterpenation concentrates the essential oil aldehydes) or for regulatory reasons (furocoumarins withdrawal, photosensitizers ...).
The lemon tree is also at the origin of another essential oil, obtained from its leaves, called Petitgrain Lemon EO.
The harvest usually takes place between the months of November and May, although it is possible to obtain fruit all year round. The fruits are harvested mechanically before they are washed and sent to a sfumatrice. The machine breaks the zest to collect the essential oil. This oil is driven to a centrifuge by a stream of water and centrifuged twice after the filtration of the residual zest. The zest is collected to be steam distilled during 4 hours. Thus, one oil is obtained by cold press, and another by steaming.
The extraction yield of lemon zest is between 0.3 and 0.5%.
It is also possible to perform a less common hydrodistillation, starting from the fresh peel. For this method, the fruit passes directly into a peeling machine to separate the zest from the pulp and extract the fruit peel only.
The essential oil can be deterpened or desesquiterpened, to increase the intensity (a deterpenation concentrates the essential oil aldehydes) or for regulatory reasons (furocoumarins withdrawal, photosensitizers ...).
The lemon tree is also at the origin of another essential oil, obtained from its leaves, called Petitgrain Lemon EO.
Major Components :
D-Limonene (65-70%)
Beta-Pinene (10-15%)
Gamma-Terpinene (≈10%)
Citral (≈4%)
Myrcene (≈2%)
Sabinene (≈2%)
Géranial (≈1%)
Beta-Pinene (10-15%)
Gamma-Terpinene (≈10%)
Citral (≈4%)
Myrcene (≈2%)
Sabinene (≈2%)
Géranial (≈1%)
- Uses in perfumery :
- Used in eaux fraîches, colognes, citrus flavours. Brings freshness and head, sometimes with other citrus fruits. Matches well with Hedione®.
- Other comments :
- Lemon is particularly grown in Sicily where it is found since it was introduced by the Arabs during the tenth century.
The Sicily mountaneous area does not allow too big areas of cultivation, the fields are smaller than those of California (2nd world producer).
Citrus currently suffer from a disease called ''citrus greening ''. This disease is deadly for citrus fruits and no treatment exists. It is transmitted by a vector insect that attacks young shoots: the psylla. This results in the premature death of many trees and therefore the decline in the general production of the essential oil and its quality (reduction of the D-Limonene level). - Volatility :
- Head
- Appearance :
- Pale yellow liquid
- Stability :
- Solubility issues in perfumes
Citruses tend to fade through time in perfumes
Limonene tends to convert into Carvone through time, and to give a minthy note to the oil
Aldehydes can form diethylacetals in stability tests, without modifying the raw material’s smell - Price Range :
- €€
- Aromatherapy :
Informations provided below are taken from reference works in aromatherapy. They are given for information purposes only and can not constitute medical information, nor engage the responsibility of ScenTree.
Lemon has antibacterial, antiseptic, litholytic and soothing properties. It is recommended in case of liver failure (difficulty of action of the liver), digestive insufficiency, renal colic (obstruction of the urinary tract) and to disinfect the air of a room.
Crédits photo: ScenTree SAS
- EINECS number :
- 84929-31-7
- FEMA number :
- 2625
- Allergens :
- D-Limonene - Citral - Linalool - Geraniol - Citronellol
- IFRA :
- This ingredient is restricted by IFRA
- Restriction type :
- RESTRICTION
- Cause of restriction :
- PHOTOTOXICITY
- Amendment :
- 49
- Comments :
- The Standard is set due to the phototoxic effects of Lemon oil cold pressed. For more detailed information on the application of this Standard, please refer to the note on phototoxic ingredients in chapter 1 of the Guidance for the use of IFRA Standards. If the level of furocoumarins is unknown, the restriction level specified in this IFRA Standard applies. Combination effects of phototoxic ingredients are only taken into consideration for the furocoumarin-containing fragrance ingredients (extracts) listed in the IFRA Standard of Citrus oils and other furocoumarins containing essential oils. If combinations of furocoumarin-containing phototoxic fragrance ingredients (extracts) are used, the use levels must be reduced accordingly. The sum of the concentrations of all furocoumarin-containing phototoxic fragrance ingredients (extracts), expressed in of their recommended upper concentration level in the consumer product shall not exceed 100. For qualities of the expressed oil in which the less volatile components have been concentrated by partial or total removal of the terpene fraction, this limit should be reduced in proportion to the degree of concentration.
- Quantitative limit on the use :
-
Cat.1 Cat.2 Cat.3 Cat.4 Cat.5A Cat.5B Cat.5C Cat.5D Cat.6 2 % 2 % 2 % 2 % 2 % 2 % 2 % 2 % 2 % Cat.7A Cat.7B Cat.8 Cat.9 Cat.10A Cat.10B Cat.11A Cat.11B Cat.12 No Restriction 2 % 2 % No Restriction No Restriction 2 % No Restriction 2 % No Restriction - Annexe I :
- Some regulated synthetic ingredients are found in nature and in certain proportions in natural ingredients. This presence in nature has to be taken into account when calculating limits of use recommended by the IFRA. In case you do not know these concentrations, you can use the ones estimated by the IFRA. Here they are :
- Restriction type :
- RESTRICTION NON QRA
- Cause of restriction :
- PHOTOTOXICITY
- Amendment :
- 48
- Comments :
- The limit only applies to applications on skin exposed to sunshine, excluding rinse-off products (please refer to Table 4 of the QRA booklet for more detailed information). If combinations of phototoxic fragrance ingredients are used, the use levels have to be reduced accordingly. The sum of the concentrations of all phototoxic ingredients, expressed in % of their recommended maximum level in the consumer product shall not exceed 100. Note: See remark on phototoxic ingredients in the Introduction to the IFRA Standards (Appendix 8 to the IFRA Code of Practice) and the Standard on Citrus oil and other furocoumarins-containing essential oils. For qualities of the expressed oil in which less volatile components have been concentrated by partial or total removal of the terpene fraction, this limit should be reduced in proportion to the degree of concentration.
- Annexe I :
- Some regulated synthetic ingredients are found in nature and in certain proportions in natural ingredients. This presence in nature has to be taken into account when calculating limits of use recommended by the IFRA. In case you do not know these concentrations, you can use the ones estimated by the IFRA. Here they are :
| List of regulated compounds contained in this ingredient | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regulated ingredient name | CAS N° | Estimated Concentration |
| Citronellal | 106-23-0 | 0,1 |
| Geraniol | 106-24-1 | 0,1 |
| Citral | 5392-40-5 | 2,1 |
| Skin contact products | Non skin contact products | |
|---|---|---|
| Leave on products | Rinse off products | |
| 2 % | X | X |
| List of regulated compounds contained in this ingredient | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regulated ingredient name | CAS N° | Estimated Concentration |
| Citronellal | 106-23-0 | 0,1 |
| Geraniol | 106-24-1 | 0,1 |
| Citral | 5392-40-5 | 2,1 |
To learn more about IFRA's standards : https://ifrafragrance.org/safe-use/library
ScenTree is solely responsible for the information provided here.





