Scots Pine Absolute
Naturelle
Woody > Coniferous > Balsamic > Grassy > Animalic

Crédits photo: ScenTree SAS
Latin name :
Pinus Sylvestris
Botanical profile :
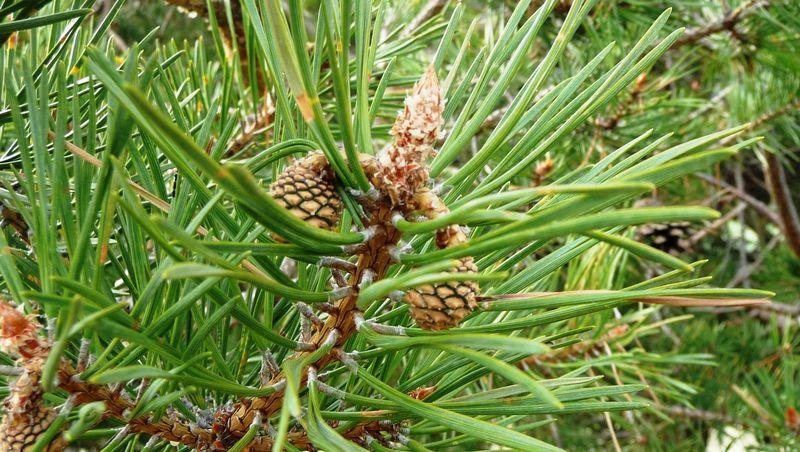
Scots pine is a species of pine of the Pinaceae family and the genus Pinus.
Geographic origin :
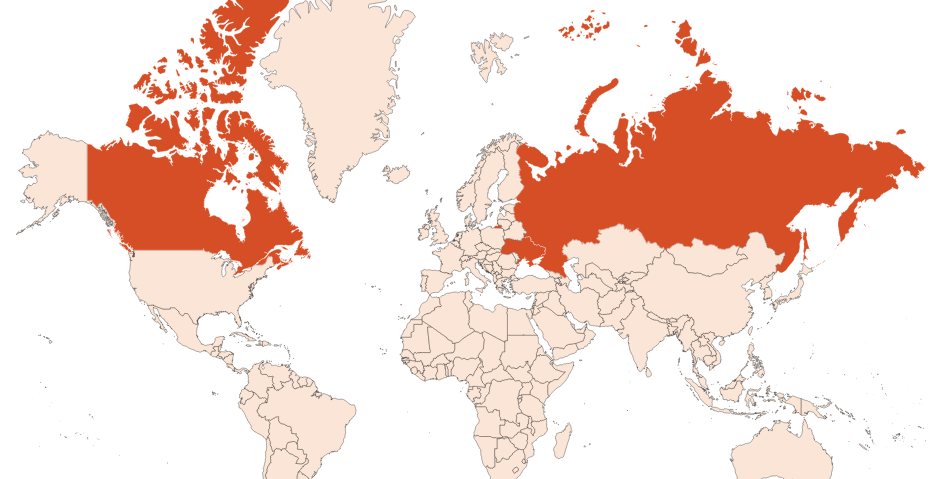
Native to Asia and Europe, Scots pine is grown in Russia, Canada, France and the USA.
Chemotypes :
Scots pine has two different chemotypes: one is ssp. sylvetris and the other contains δ-3-Carene.
Other pines are commonly used in perfumery including:
The longleaf Indian pine from the Himalayas (Pinus roxburghii); the black pine (Pinus nigra), whose two subspecies are the laricio pine of Corsica and Calabria, and the black pine of Austria; the Swiss pine (Pinus cembra); the mountain pine (Pinus montana); the maritime pine (Pinus pinaster); the longleaf pine (Pinus palustris) are pines originating in Eurasia, such as the Scots pine.
The white pine (Pinus strobus), the red pine (Pinus resinosa), the jack pine (Pinus divaricata) and the western yellow pine (Pinus ponderosa) are pines from North America.
The difference made between a pine (genus Pinus) and a fir (genus Abies) lies in the arrangement of their needles: the needles of the pine inserted in groups of two, three or five, and the needles of the fir are arranged one by one to the twigs.
Other pines are commonly used in perfumery including:
The longleaf Indian pine from the Himalayas (Pinus roxburghii); the black pine (Pinus nigra), whose two subspecies are the laricio pine of Corsica and Calabria, and the black pine of Austria; the Swiss pine (Pinus cembra); the mountain pine (Pinus montana); the maritime pine (Pinus pinaster); the longleaf pine (Pinus palustris) are pines originating in Eurasia, such as the Scots pine.
The white pine (Pinus strobus), the red pine (Pinus resinosa), the jack pine (Pinus divaricata) and the western yellow pine (Pinus ponderosa) are pines from North America.
The difference made between a pine (genus Pinus) and a fir (genus Abies) lies in the arrangement of their needles: the needles of the pine inserted in groups of two, three or five, and the needles of the fir are arranged one by one to the twigs.
Extraction process :
Scots pine can grow up to 40 metres high on poor, siliceous soils. The part treated to obtain the essential oil of Scots pine is its branches of needles. The tree is generally grown from July to September in Siberia. The month of harvest can have an influence on the composition of the essential oil.
Whole trees are uprooted in order to easily separate the needle branches from the wood of the tree, that is used in other industries. Generally, machines used to uproot trees also make it possible to ''shave '' the trunk and remove branches and twigs.
At the factory, the needle branches are directly introduced into the extractor. A first extraction takes place, using hexane. This solvent makes it possible to obtain a pine concrete in a few hours, following the removal of the branches from the extractor, and the solvent by evaporation. This concrete is then chilled in alcohol, imposing a temperature ramp from 60°C to 0°C to the mixture to precipitate the waxes. By filtration, then evaporation of the solvent, the pine absolute is obtained.
Often, the resin of the wood is used to extract Turpentine EO, which has a high added value and a stronger smell. In addition, steam distillation of the dried twigs makes it possible to obtain Scots Pine EO.
Whole trees are uprooted in order to easily separate the needle branches from the wood of the tree, that is used in other industries. Generally, machines used to uproot trees also make it possible to ''shave '' the trunk and remove branches and twigs.
At the factory, the needle branches are directly introduced into the extractor. A first extraction takes place, using hexane. This solvent makes it possible to obtain a pine concrete in a few hours, following the removal of the branches from the extractor, and the solvent by evaporation. This concrete is then chilled in alcohol, imposing a temperature ramp from 60°C to 0°C to the mixture to precipitate the waxes. By filtration, then evaporation of the solvent, the pine absolute is obtained.
Often, the resin of the wood is used to extract Turpentine EO, which has a high added value and a stronger smell. In addition, steam distillation of the dried twigs makes it possible to obtain Scots Pine EO.
Major Components :
Data not available.
- Uses in perfumery :
- Used in leather, woody and oriental notes, to bring a sweet and oriental facet.
- Other comments :
- The difference between a pine tree and a fir tree is made in the grouping of their needles. In the case of pine, they are grouped and attached to the branches. In the case of fir, they are independently attached to the branches.
Very often, pine essential oil and turpentine oil allow the extraction of various terpenes such as pinene, carene and many others.
Volatile solvent extraction of a pine brings a very different chromatographic profile as for an essential oil. The resulting smell is warmer, more caramelized and less terpenic than an essential oil. - Volatility :
- Base
- Appearance :
- Dark green liquid
- Stability :
- Terpenes present in this essential oil are subjected to polymerization under the effect of a strong oxydation.
- Price Range :
- €€€€
- Aromatherapy :
Informations provided below are taken from reference works in aromatherapy. They are given for information purposes only and can not constitute medical information, nor engage the responsibility of ScenTree.
Scots pine essential oil is known to act as cortisone, on the pituitary-cortico-adrenal axis (HHS axis), and thus helps to gain energy. It is recommended for use in cases of asthenia (lack of strength), bronchitis and sinusitis.
Crédits photo: ScenTree SAS
- EINECS number :
- 84012-35-1
- FEMA number :
- 2906
- Allergens :
- This ingredient does not contain any allergen.
- IFRA :
- This ingredient is not restricted
To learn more about IFRA's standards : https://ifrafragrance.org/safe-use/library
ScenTree is solely responsible for the information provided here.

