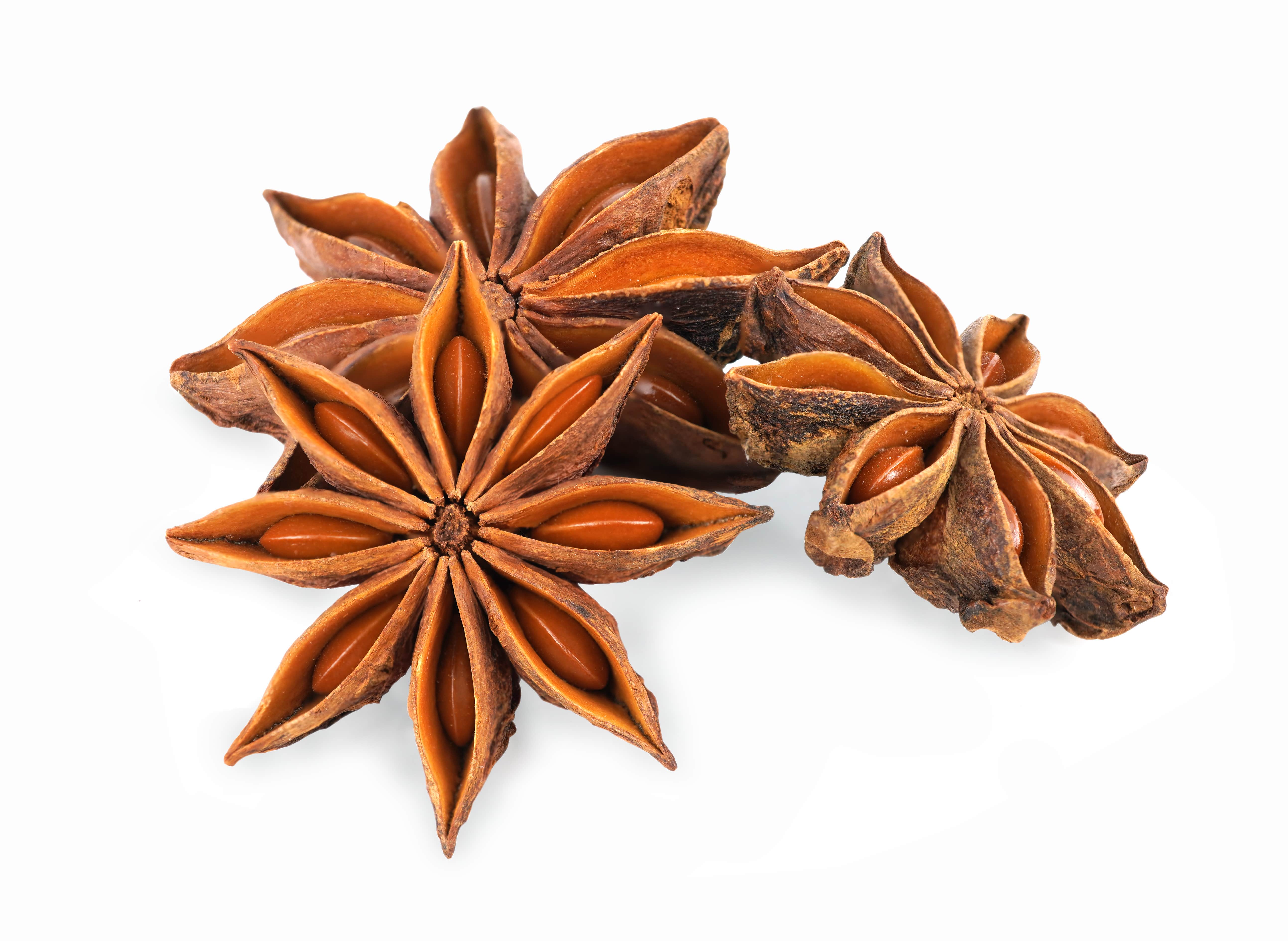
Star Anise EO
Naturelle
Herbal > Anisic > Warm Woods

Crédits photo: ScenTree SAS
Latin name :
Illicium verum
Botanical profile :
The star anise is the fruit of the star anise tree, from the family of the Illicaceae and the genus Illicium (Latin name meaning ''attractive '').
Geographic origin :
Initialy originated from China, star anise was introduced in Europe at the end of the 16th century.
Other productor : Cambodge, Laos, Japon, Phillipines.
Other productor : Cambodge, Laos, Japon, Phillipines.
Chemotypes :
Illicium anisatum, also called Japanese aniseed tree is very toxic but is not grown for essential oil extraction, nor for edible purposes. The Japanese use it as incense. This variety also contains Safrole and Eugenol, two compounds that are not present in Illicium verum and are used to detect contamination of star anise lots.
Extraction process :
This spice is famous worldwide for its taste but also for its essential oil. It owes its name to its peculiar form consisting of a woody follicle with eight carpels, each containing a seed. The tree on which this star grows can reach 10 meters tall.
The propagation of a star anise crop is done by sowing seeds, directly visible in the fruits. The tree is cultivated outside of the field at first and planted in the field, every five meters, after three years of growth.
Harvests occur two to three times a year, in April and October. The fruits are usually picked green and sun-dried for 7 to 8 hours, until they become red-brown and lose 75% of their weight. The older the tree, the more important the harvest: a 15 year old tree can reach 20kg of fruit per year.
To collect the essential oil, seeds and bark (or seeds alone) are steam distilled for about : 48h for fresh fruits (yield: 2 to 4%) or 60h for dry fruits (yield: 8 to 9%).
Extraction can also be done with volatile solvents or with supercritical CO2 with a yield of about 10% but a higher quality of essential oil.
The propagation of a star anise crop is done by sowing seeds, directly visible in the fruits. The tree is cultivated outside of the field at first and planted in the field, every five meters, after three years of growth.
Harvests occur two to three times a year, in April and October. The fruits are usually picked green and sun-dried for 7 to 8 hours, until they become red-brown and lose 75% of their weight. The older the tree, the more important the harvest: a 15 year old tree can reach 20kg of fruit per year.
To collect the essential oil, seeds and bark (or seeds alone) are steam distilled for about : 48h for fresh fruits (yield: 2 to 4%) or 60h for dry fruits (yield: 8 to 9%).
Extraction can also be done with volatile solvents or with supercritical CO2 with a yield of about 10% but a higher quality of essential oil.
Major Components :
Anethole (85-90%)
D-Limonene (≈3%)
Estragole (≈3%)
Linalool (≈1%)
D-Limonene (≈3%)
Estragole (≈3%)
Linalool (≈1%)
- Uses in perfumery :
- Gives depth to fougere, citrus, aromatic and chypre notes. Also used in spicy bouquets, liquorice notes and to give naturalness to green notes.
- Other comments :
- The essential oil of star anise is distinguished from the green anise oil by its Fenchone content.
The adulteration of the essential oil is possible by adding synthetic Anethole (less expensive) which is the essential oil of Japanese star anise (more toxic ...), although its use is highly regulated. Controls are made by chemical analysis to check its rate.
The essential oil of star anise is generally used to isolate the natural Anethole. The essential oil can be subjected to an ozonolysis process to remove anisaldehyde. In this operation, almost all the anethole included in the essential oil is converted to anisaldehyde. - Volatility :
- Heart
- Appearance :
- Colorless liquid
- Stability :
- Aromatic compounds can be chromophoric and cause a coloration of the oil, especially in alkaline bases
The terpenes identified in this raw material can polymerize when they are oxidized - Price Range :
- €€
- Aromatherapy :
Informations provided below are taken from reference works in aromatherapy. They are given for information purposes only and can not constitute medical information, nor engage the responsibility of ScenTree.
Antispasmodic, tonic and stimulant, star anise also relieves coughs, bronchitis and rheumatism.
Crédits photo: ScenTree SAS
- EINECS number :
- 283-872-7
- FEMA number :
- 2094
- Allergens :
- This ingredient does not contain any allergen.
- IFRA :
- This ingredient is restricted by IFRA
- Annexe I :
- Some regulated synthetic ingredients are found in nature and in certain proportions in natural ingredients. This presence in nature has to be taken into account when calculating limits of use recommended by the IFRA. In case you do not know these concentrations, you can use the ones estimated by the IFRA. Here they are :
- Annexe I :
- Some regulated synthetic ingredients are found in nature and in certain proportions in natural ingredients. This presence in nature has to be taken into account when calculating limits of use recommended by the IFRA. In case you do not know these concentrations, you can use the ones estimated by the IFRA. Here they are :
| List of regulated compounds contained in this ingredient | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regulated ingredient name | CAS N° | Estimated Concentration |
| p-Methoxybenzaldehyde | 123-11-5 | 1 |
| Estragole | 140-67-0 | 0,3 |
| List of regulated compounds contained in this ingredient | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regulated ingredient name | CAS N° | Estimated Concentration |
| p-Methoxybenzaldehyde | 123-11-5 | 1 |
| Estragole | 140-67-0 | 0,3 |
To learn more about IFRA's standards : https://ifrafragrance.org/safe-use/library
ScenTree is solely responsible for the information provided here.




