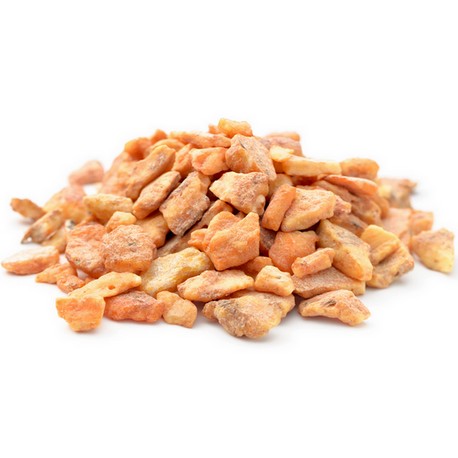
Sumatra Benzoin Resinoid
Naturelle
Balsamic Ambery > Balsamic > Vanillic > Warm Woods

Crédits photo: ScenTree SAS
Latin name :
Styrax benzoin
Botanical profile :
Benzoin is a resin gum from trees of the Styracaceae family and the genus Styrax.
Geographic origin :
Originally from the island of Sumatra, Indonesia, this benzoin is grown mainly in Malaysia and Indonesia.
Chemotypes :
The Styrax family includes about 130 species found mainly in Southeast Asia or South America.
Two varieties of Benzoin are used in perfumery:
Styrax tonkinensis so called Siam Benzoin Resinoid
Styrax benzoin so called Sumatra Benzoin Resinoid
Sumatra benzoin is more used than the Siam Benzoin because it is spicier and has a softer vanilla scent.
Two varieties of Benzoin are used in perfumery:
Styrax tonkinensis so called Siam Benzoin Resinoid
Styrax benzoin so called Sumatra Benzoin Resinoid
Sumatra benzoin is more used than the Siam Benzoin because it is spicier and has a softer vanilla scent.
Extraction process :
The benzoin producing trees are about 25 meters high and grow at more than 1500 meters altitude. Farmers start exploiting the trees when they reach the age of 8 for Siam and 25 for Sumatra, lasting about 10 years.
The gum-resin is obtained by a voluntary incision on the barks of the tree. This incision causes the exsudation of a milky resin which solidifies by oxidation when in contact with air. Harvesting is done by scratching the teardrops for a yield of 4 to 6 kg per tree per year.
Finally, the gums are extracted with organic solvent (ethanol) to obtain the resinoid by filtration after glazing (temperature gradient from 140 °F to 32 °F) the center.
It is very unusual to obtain an essential oil of benzoin by hydrodistillation.
The benzoin resinoid can be distilled to be bleached, without a great olfactory deterioration.
The gum-resin is obtained by a voluntary incision on the barks of the tree. This incision causes the exsudation of a milky resin which solidifies by oxidation when in contact with air. Harvesting is done by scratching the teardrops for a yield of 4 to 6 kg per tree per year.
Finally, the gums are extracted with organic solvent (ethanol) to obtain the resinoid by filtration after glazing (temperature gradient from 140 °F to 32 °F) the center.
It is very unusual to obtain an essential oil of benzoin by hydrodistillation.
The benzoin resinoid can be distilled to be bleached, without a great olfactory deterioration.
Major Components :
Cinnamic Esters (70-80%)
Cinnamic Acid (15-20%)
Vanillin (≈1%)
Plotter(s) : Ethoxy Coniferol (or Coniferyl Ethyl Ether) (≈2%)
Cinnamic Acid (15-20%)
Vanillin (≈1%)
Plotter(s) : Ethoxy Coniferol (or Coniferyl Ethyl Ether) (≈2%)
- Uses in perfumery :
- Used in oriental, vanilla, caramel, chocolate, exotic-ylang and tuberose notes for a warm and enveloping effect.
- Other comments :
- In some countries, Benzoin is listed as an E906 food additive, but it is not allowed in France. Please note that Sumatra Island also cultivate Styrax Paralleloneurum but this variety is not used in perfumery.
- Volatility :
- Base
- Appearance :
- Ochre to amber resin
- Stability :
- Solubility issues in perfumes
The esters identified in this raw material can form their corresponding acid in stability tests
Not to be used in a candle base, it unlights the fire. - Price Range :
- €€€
- Aromatherapy :
Informations provided below are taken from reference works in aromatherapy. They are given for information purposes only and can not constitute medical information, nor engage the responsibility of ScenTree.
The benzoin are known for their healing virtues, pulmonary antiseptics, in cases of dermatological disorders (dermatoses, acne ...) and catarrhal respiratory diseases (bronchitis).
Crédits photo: ScenTree SAS
- EINECS number :
- 232-523-7
- FEMA number :
- 2133
- Allergens :
- Cinnamyl Alcohol - Cinnamates
- IFRA :
- This ingredient is restricted by IFRA
- Annexe I :
- Some regulated synthetic ingredients are found in nature and in certain proportions in natural ingredients. This presence in nature has to be taken into account when calculating limits of use recommended by the IFRA. In case you do not know these concentrations, you can use the ones estimated by the IFRA. Here they are :
- Annexe I :
- Some regulated synthetic ingredients are found in nature and in certain proportions in natural ingredients. This presence in nature has to be taken into account when calculating limits of use recommended by the IFRA. In case you do not know these concentrations, you can use the ones estimated by the IFRA. Here they are :
| List of regulated compounds contained in this ingredient | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regulated ingredient name | CAS N° | Estimated Concentration |
| Benzyl cinnamate | 103-41-3 | 0,8 |
| Benzyl benzoate | 120-51-4 | 0,6 |
| List of regulated compounds contained in this ingredient | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regulated ingredient name | CAS N° | Estimated Concentration |
| Benzyl cinnamate | 103-41-3 | 0,8 |
| Benzyl benzoate | 120-51-4 | 0,6 |
To learn more about IFRA's standards : https://ifrafragrance.org/safe-use/library
ScenTree is solely responsible for the information provided here.




