Ceylon Cinnamon EO
Naturelle
Spicy > Warm Spices > Cinnamic > Eugenolic > Zesty
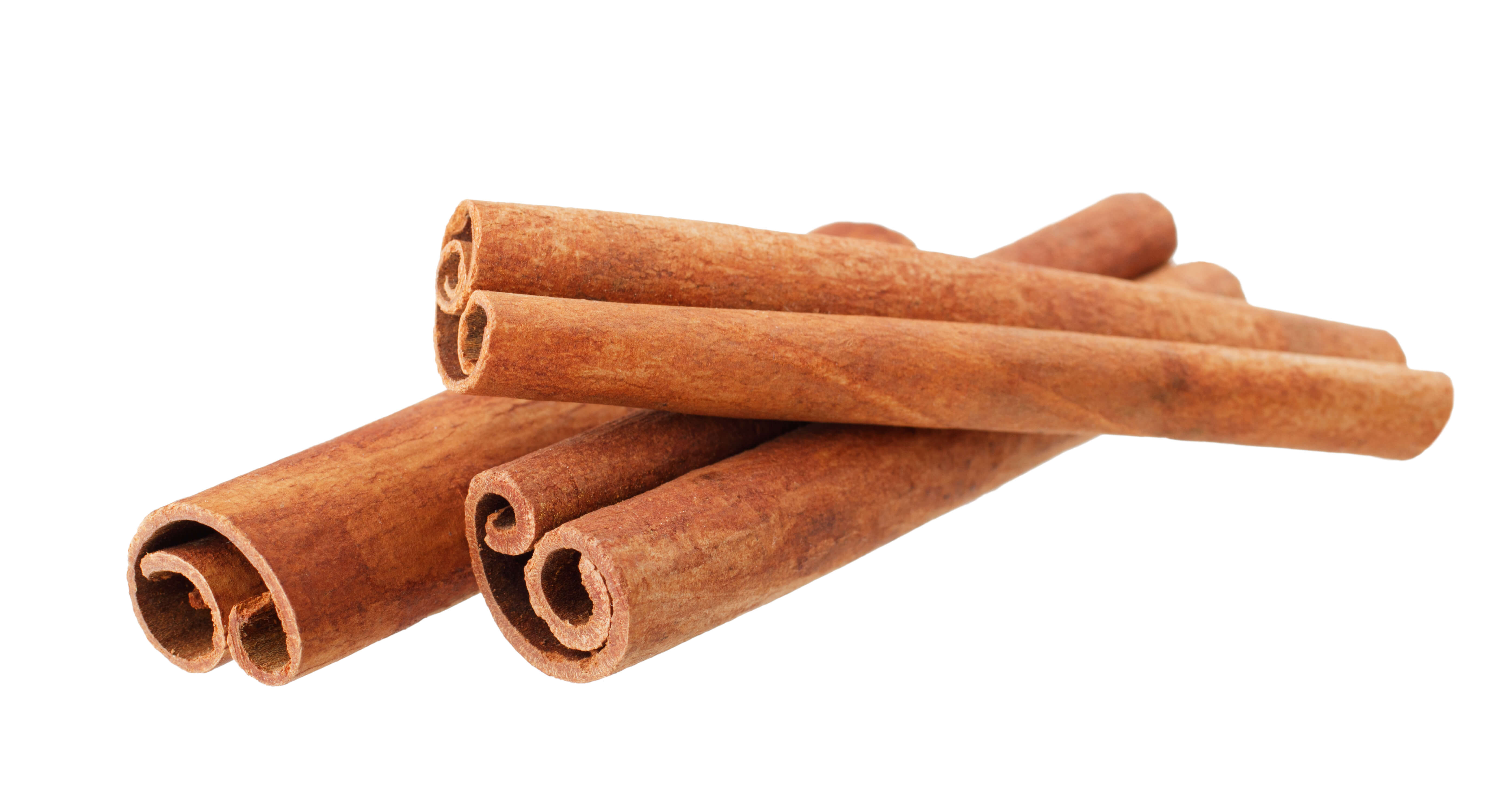

Crédits photo: ScenTree SAS
Latin name :
Cinnamomum zeylanicum
Botanical profile :
Cinnamon is the bark of the cinnamon tree, belonging to the Lauraceae family and the Cinnamomum genus.
Geographic origin :
Ceylon cinnamon trees grow at low altitudes in parts of Sri Lanka.
Chemotypes :
There are more than 250 species of cinnamon trees throughout Southeast Asia, China and Australia. The perfume industry generally uses only two of those varieties of cinnamon:
Cinnamomum zeylanicum : Ceylon cinnamon EO. Leaves are extracted.
Cinnamomum cassia : Chinese cinnamon or Cassia EO. Leaves from this tree are not extracted for perfumery.
We can also distinguish Cinnamomum burmanni : Korintje cassia SFE and Cinnamomum tamala : Indian cinnamon, much less cultivated.
The difference between the two types of cinnamon lies in the way they are dried. Cassia dries forming two spirals, whereas Ceylon cinnamon forms thin layers of wood which crumble easily. The chinese variety is also darker and harder. Ceylon cinnamon has a more zesty and terpenic smell than the Chinese cinnamon, which contains more Cinnamaldehyde.
Cinnamomum zeylanicum : Ceylon cinnamon EO. Leaves are extracted.
Cinnamomum cassia : Chinese cinnamon or Cassia EO. Leaves from this tree are not extracted for perfumery.
We can also distinguish Cinnamomum burmanni : Korintje cassia SFE and Cinnamomum tamala : Indian cinnamon, much less cultivated.
The difference between the two types of cinnamon lies in the way they are dried. Cassia dries forming two spirals, whereas Ceylon cinnamon forms thin layers of wood which crumble easily. The chinese variety is also darker and harder. Ceylon cinnamon has a more zesty and terpenic smell than the Chinese cinnamon, which contains more Cinnamaldehyde.
Extraction process :
In Sri Lanka, 24,000 hectares of forest are planted with Ceylon cinnamon. In 2006, Sri Lanka produced 90% of Ceylon cinnamon worldwide.
The leaves and the bark are mature 12 to 18 months after the preceding harvest. From red to dark green, the colour of the leaves indicates the cinnamon maturity. The culture often takes place in May and November. The bark of the cinnamon tree is very friable and can easily be detached from the trunk by sliding a knife between the two parts. The older the tree, the greater the bark yield per hectare is important. After separating the trunk, the pieces of bark are stacked, pressed and dried overnight in the shade to avoid sunburns, for four to five days. In wet weather, the use of a desiccator may be necessary. The bark shrinks, browns and develops its olfactory potential. This is when cinnamon can be extracted by steaming. The extraction is practiced on the strips of bark as such or slightly crushed. After distillation, the essential oil is collected by decantation in a florentine vase. The quality of the essential oil depends on the part of the extracted trunk. Its quality is better if it is the center of the trunk. Corrections are made to standardize the quality of the essential oil.
The distillation can be done on site, or directly by the companies that produces the essential oil, in Western Europe or in North America. France is the largest importer of Sri Lanka cinnamon essential oil, followed by the United States.
Many olfactory variations can occur depending on crops, forests and even between trees in the same forest.
Cinnamon oleoresin can be obtained from the extraction of the bark with a volatile solvent. Using ethanol gives a yield of 10 to 12%, while using benzene leads to a yield of 2 to 4%.
The leaves and the bark are mature 12 to 18 months after the preceding harvest. From red to dark green, the colour of the leaves indicates the cinnamon maturity. The culture often takes place in May and November. The bark of the cinnamon tree is very friable and can easily be detached from the trunk by sliding a knife between the two parts. The older the tree, the greater the bark yield per hectare is important. After separating the trunk, the pieces of bark are stacked, pressed and dried overnight in the shade to avoid sunburns, for four to five days. In wet weather, the use of a desiccator may be necessary. The bark shrinks, browns and develops its olfactory potential. This is when cinnamon can be extracted by steaming. The extraction is practiced on the strips of bark as such or slightly crushed. After distillation, the essential oil is collected by decantation in a florentine vase. The quality of the essential oil depends on the part of the extracted trunk. Its quality is better if it is the center of the trunk. Corrections are made to standardize the quality of the essential oil.
The distillation can be done on site, or directly by the companies that produces the essential oil, in Western Europe or in North America. France is the largest importer of Sri Lanka cinnamon essential oil, followed by the United States.
Many olfactory variations can occur depending on crops, forests and even between trees in the same forest.
Cinnamon oleoresin can be obtained from the extraction of the bark with a volatile solvent. Using ethanol gives a yield of 10 to 12%, while using benzene leads to a yield of 2 to 4%.
Major Components :
Cinnamaldehyde (70-80%)
Cinnamyl Acetate (≈5%)
Eugenol (≈2%)
Coumarin (≈2%)
Benzoic Aldehyde (≈1%)
Cinnamyl Acetate (≈5%)
Eugenol (≈2%)
Coumarin (≈2%)
Benzoic Aldehyde (≈1%)
- Uses in perfumery :
- Used in spicy, floral-carnation, cola and fruity notes for a fresh touch. Gives support to warm woody and amber notes. Very useful in Christmas fragrance collections.
- Other comments :
- The name ''Ceylon '' comes from the old name of the island located in the South of India, on which this cinnamon is cultivated: Sri Lanka.
The quality of a cinnamon bark is measured by its appearance, the constitution of its essential oil and the fineness of its chips.
A quality cinnamon contains 0.9 to 2.3% of essential oil in its bark.
Several adulterations are made adding essential oil of Chinese cinnamon to the essential oil of Ceylon cinnamon to lower the production price of the essential oil. It is also possible to add a mixture of 96% Cinnamaldehyde and 4% Eugenol. To be accepted, an essential oil of cinnamon must not contain more than 14% of Eugenol and its share of Cinnamaldehyde must not be inferior to 60%.
The essential oil of cinnamon is a major precursor to the extraction of natural Cinnamaldehyde, although it is extracted preferentially from the essential oil of Chinese cinnamon, which contains more with a more reasonable price.
The smell of cinnamon roots is more camphoric, earthy and floral than the bark. - Volatility :
- Heart/Base
- Appearance :
- Pale yellow liquid
- Stability :
- Aldehydes can form diethylacetals in stability tests, without modifying the raw material’s smell
- Price Range :
- €€€
- Aromatherapy :
Informations provided below are taken from reference works in aromatherapy. They are given for information purposes only and can not constitute medical information, nor engage the responsibility of ScenTree.
The consumption of essential oil of Ceylon cinnamon, although limited for its toxicity, is recommended in case of bronchitis, angina, warts, and for its antioxidant virtues.
Crédits photo: ScenTree SAS
- EINECS number :
- 84649-98-9
- FEMA number :
- 2291
- Allergens :
- Cinnamaldehyde - Cinnamyl Alcohol - Eugenol - Linalool
- IFRA :
- This ingredient is restricted by IFRA
- Annexe I :
- Some regulated synthetic ingredients are found in nature and in certain proportions in natural ingredients. This presence in nature has to be taken into account when calculating limits of use recommended by the IFRA. In case you do not know these concentrations, you can use the ones estimated by the IFRA. Here they are :
- Annexe I :
- Some regulated synthetic ingredients are found in nature and in certain proportions in natural ingredients. This presence in nature has to be taken into account when calculating limits of use recommended by the IFRA. In case you do not know these concentrations, you can use the ones estimated by the IFRA. Here they are :
| List of regulated compounds contained in this ingredient | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regulated ingredient name | CAS N° | Estimated Concentration |
| Benzaldehyde | 100-52-7 | 0,2 |
| Cinnamyl acetate | 103-54-8 | 5 |
| Cinnamic alcohol | 104-54-1 | 0,3 |
| Cinnamic aldehyde | 104-55-2 | 75 |
| Benzyl benzoate | 120-51-4 | 0,6 |
| o-Methoxycinnamaldehyde | 1504-74-1 | 0,5 |
| Coumarin | 91-64-5 | 0,6 |
| Safrole | 94-59-7 | 0,2 |
| Eugenol | 97-53-0 | 2 |
| Isoeugenol | 97-54-1 | 0,02 |
| List of regulated compounds contained in this ingredient | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regulated ingredient name | CAS N° | Estimated Concentration |
| Benzaldehyde | 100-52-7 | 0,2 |
| Cinnamyl acetate | 103-54-8 | 5 |
| Cinnamic alcohol | 104-54-1 | 0,3 |
| Cinnamic aldehyde | 104-55-2 | 75 |
| Benzyl benzoate | 120-51-4 | 0,6 |
| o-Methoxycinnamaldehyde | 1504-74-1 | 0,5 |
| Coumarin | 91-64-5 | 0,6 |
| Safrole | 94-59-7 | 0,2 |
| Eugenol | 97-53-0 | 2 |
| Isoeugenol | 97-54-1 | 0,02 |
To learn more about IFRA's standards : https://ifrafragrance.org/safe-use/library
ScenTree is solely responsible for the information provided here.



