Cistus Absolute
Naturelle
Burnt Leather > Burnt > Plastic

Crédits photo: ScenTree SAS
Latin name :
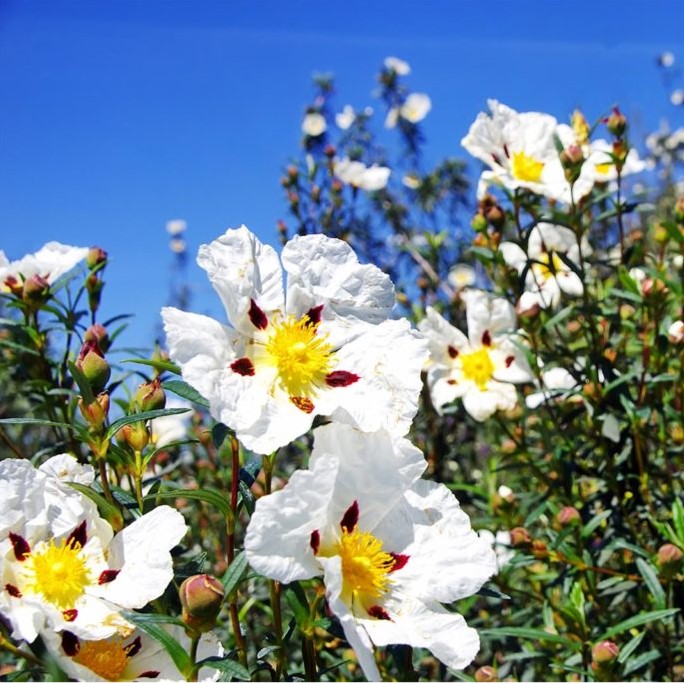
Cistus ladaniferus L.
Botanical profile :
The cistus belongs to the Cistaceae family and to the genus Cistus. This includes three subspecies.
Geographic origin :
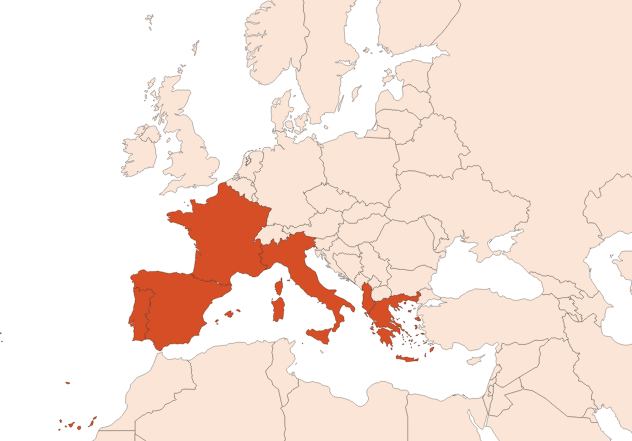
Cistus ladaniferus is a common plant found all over the mediterranean area. It is especially abundant in Spain ( Huelva Province - Andevalo) as well as in Portugal (Alentejo and Algarve regions). This is where the largest cistus plantations are located. It is also possible to find some cultivations in the Esterel (Var - France).
The emblematic city of Cistus is Puebla de Guzman, in Andalusia, where the communities, mainly gypsies, have transmitted a unique savoir-faire from one generation to the next.
The emblematic city of Cistus is Puebla de Guzman, in Andalusia, where the communities, mainly gypsies, have transmitted a unique savoir-faire from one generation to the next.
Chemotypes :
The genus Cistus includes about 20 different species, the majority of which exudes fragrant gum.
Among these, the most used are:
Cistus ladaniferus var. albiflorus, var. maculatos, var. stenoiphyllus, which produce the resin used in perfumes.
Cistus creticus, with rose to purple petals, surronding a tuft of stamens.
Cistus salvifolius, with white petals.
Cistus parviflorus, with pale rose petals.
Among these, the most used are:
Cistus ladaniferus var. albiflorus, var. maculatos, var. stenoiphyllus, which produce the resin used in perfumes.
Cistus creticus, with rose to purple petals, surronding a tuft of stamens.
Cistus salvifolius, with white petals.
Cistus parviflorus, with pale rose petals.
Extraction process :
In April, Cistus ladaniferus fields are covered with the famous white flowers, but they don't smell and are very delicate (they only last a few days). It is necessary to wait a few months, around May-June, for a new shoot to appear. This new branch protects itself from the sun - and from the summer heat of southern Spain - by secreting a very fragrant viscous gum. We use the latter in perfumery.
In July, from dawn to noon, new branches are cut with a sickle, bundled and taken to the factory to extract the gum. It will then be necessary to wait another 3 years to harvest the cistus again.
To obtain the resinoid, the gum is treated in a soda solution for extraction with a 3 to 5% yield. After filtration, an acid treatment is carried out. A pasty product is recovered by skimming and distilled to dry it. The paste is finally treated with alcohol, then filtered to remove insoluble compounds. A ''labdanum alcohol resinoid '' is then obtained.
Several reprocessing are possible on the cistus absolute, to remove insoluble compounds or colour. Such rectification has no olfactory impact.
In July, from dawn to noon, new branches are cut with a sickle, bundled and taken to the factory to extract the gum. It will then be necessary to wait another 3 years to harvest the cistus again.
To obtain the resinoid, the gum is treated in a soda solution for extraction with a 3 to 5% yield. After filtration, an acid treatment is carried out. A pasty product is recovered by skimming and distilled to dry it. The paste is finally treated with alcohol, then filtered to remove insoluble compounds. A ''labdanum alcohol resinoid '' is then obtained.
Several reprocessing are possible on the cistus absolute, to remove insoluble compounds or colour. Such rectification has no olfactory impact.
Major Components :
Data not available.
- Uses in perfumery :
- Data not available.
- Other comments :
- Data not available.
- Volatility :
- Base
- Appearance :
- Brown resin
- Stability :
- Solubility issues in perfumes
The terpenes identified in this raw material can polymerize when they are oxidized - Price Range :
- Donnée indisponible.
- Aromatherapy :
Informations provided below are taken from reference works in aromatherapy. They are given for information purposes only and can not constitute medical information, nor engage the responsibility of ScenTree.
CIstus possesses antiviral, antiarteritic and regulating neurovegetative virtues. It is recommended for whooping cough, multiple sclerosis, arteritis, haemorrhage and neurovegetative dystonia.
Crédits photo: ScenTree SAS
- EINECS number :
- 934-780-7
- FEMA number :
- 2608
- Allergens :
- This ingredient does not contain any allergen.
- IFRA :
- This ingredient is restricted by IFRA
- Annexe I :
- Some regulated synthetic ingredients are found in nature and in certain proportions in natural ingredients. This presence in nature has to be taken into account when calculating limits of use recommended by the IFRA. In case you do not know these concentrations, you can use the ones estimated by the IFRA. Here they are :
| List of regulated compounds contained in this ingredient | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regulated ingredient name | CAS N° | Estimated Concentration |
| Benzaldehyde | 100-52-7 | 0,6 |
This ingredient is not restricted for the 48th amendment
To learn more about IFRA's standards : https://ifrafragrance.org/safe-use/library
ScenTree is solely responsible for the information provided here.



