Laurel EO
Naturelle
Herbal > Agrestic > Spicy > Camphoric

Crédits photo: ScenTree SAS
Latin name :
Laurus nobilis
Botanical profile :
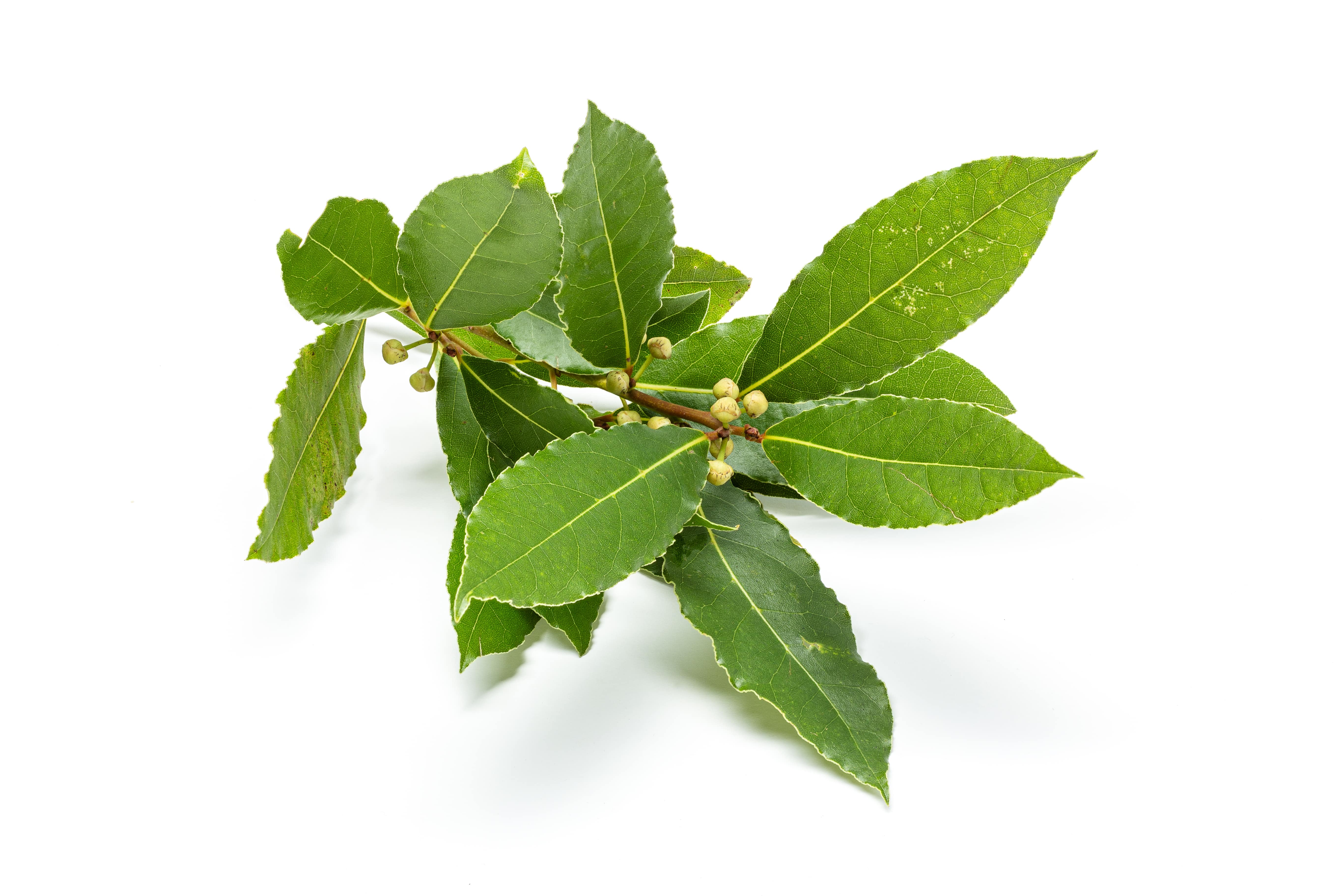
Laurel is a shrub belonging to the Lauraceae family and the genus Laurus.
Geographic origin :
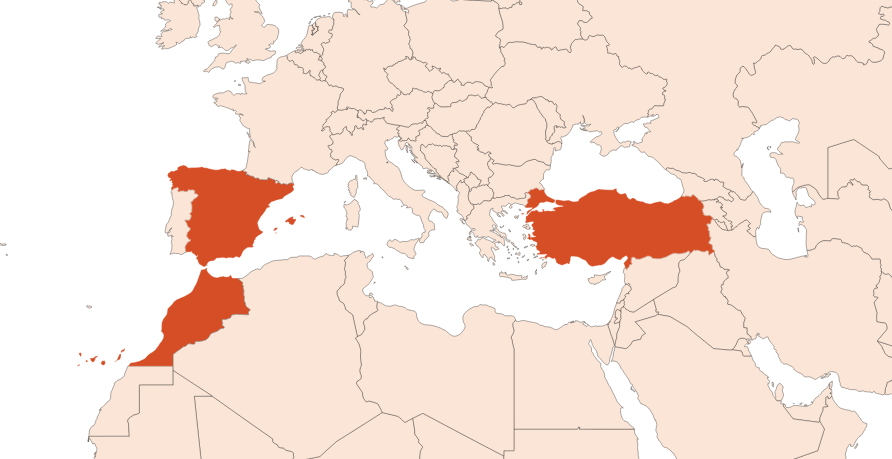
Native to Asia Minor, the plant is mainly cultivated around the Mediterranean sea, particularly in Spain, Turkey and Morocco.
Chemotypes :
Only two other species belong to the genus Laurus: Laurus azorica and Laurus canariensis. However, they are not extracted in perfumery.
There are other plants called laurel although they are not part of the genus Laurus : the California laurel, Umbellucaria californica, for example, has a toxic essential oil. The laurel clover, Cryptocaria pretiosa, the oleander, Nerium oleander and the laurel tree, Viburnum tinus, can be mentioned among others.
There are other plants called laurel although they are not part of the genus Laurus : the California laurel, Umbellucaria californica, for example, has a toxic essential oil. The laurel clover, Cryptocaria pretiosa, the oleander, Nerium oleander and the laurel tree, Viburnum tinus, can be mentioned among others.
Extraction process :
The bay is a shrub 3 to 5 meters high, conical or pyramidal. It flowers in spring and early summer, although only the leaves are processed in perfumery. The development of a laurel crop is done by seeds sowing, bringing a great variability in the pace of the plants. To solve this problem, the seeds must be treated by removing their pericarp before they are sown.
The laurel harvests take place in October and November. The leaves are crushed and dried. The nature and the temperature of the drying step has no great importance, as they do not influence the volatilization of the olfactory compounds of this plant. The steam distillation of the leaves gives the essential oil, collected at the end of the process by decantation in a florentine vase. The extraction lasts up to three hours and provides a yield around 1.3%.
The laurel harvests take place in October and November. The leaves are crushed and dried. The nature and the temperature of the drying step has no great importance, as they do not influence the volatilization of the olfactory compounds of this plant. The steam distillation of the leaves gives the essential oil, collected at the end of the process by decantation in a florentine vase. The extraction lasts up to three hours and provides a yield around 1.3%.
Major Components :
Eucalyptol (35-45%)
Linalool (8-15%)
Pinenes (7-11%)
Alpha-Terpineol (2-5%)
Eugenol (≈3%)
Methyl Eugenol (≈3%)
Linalool (8-15%)
Pinenes (7-11%)
Alpha-Terpineol (2-5%)
Eugenol (≈3%)
Methyl Eugenol (≈3%)
- Uses in perfumery :
- Used in men's perfumery for spicy, fresh, camphoraceous, sweet and woody notes, to nuance a fresh and vegetal side.
- Other comments :
- The term Laurel comes from Celtic ''blaur '' which means ''green ''. The Latin name ''nobilis '' refers to the noble character of the plant, which was entrusted by the Greeks in antiquity.
Laurel is one of the major precursors of the extraction of natural Eucalyptol, by distillation of the essential oil. - Volatility :
- Head
- Appearance :
- Colorless liquid
- Stability :
- Solubility issues in perfumes
The terpenes identified in this raw material can polymerize when they are oxidized - Price Range :
- €€€
- Aromatherapy :
Informations provided below are taken from reference works in aromatherapy. They are given for information purposes only and can not constitute medical information, nor engage the responsibility of ScenTree.
The essential oil of laurel can be used as expectorant (causes cough), analgesic, balancing and is indicated in case of influenza, arthritis, adenitis (ganglionic inflammation), dental pain and apthosis (violent growth of the teeth).
Crédits photo: ScenTree SAS
- EINECS number :
- 84603-73-6
- FEMA number :
- 2125
- Allergens :
- D-Limonene - Linalool - Eugenol
- IFRA :
- This ingredient is restricted by IFRA
- Annexe I :
- Some regulated synthetic ingredients are found in nature and in certain proportions in natural ingredients. This presence in nature has to be taken into account when calculating limits of use recommended by the IFRA. In case you do not know these concentrations, you can use the ones estimated by the IFRA. Here they are :
- Annexe I :
- Some regulated synthetic ingredients are found in nature and in certain proportions in natural ingredients. This presence in nature has to be taken into account when calculating limits of use recommended by the IFRA. In case you do not know these concentrations, you can use the ones estimated by the IFRA. Here they are :
| List of regulated compounds contained in this ingredient | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regulated ingredient name | CAS N° | Estimated Concentration |
| Cinnamyl acetate | 103-54-8 | 0,1 |
| Geraniol | 106-24-1 | 0,05 |
| Methyl eugenol | 93-15-2 | 3 |
| Eugenol | 97-53-0 | 1,1 |
| List of regulated compounds contained in this ingredient | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regulated ingredient name | CAS N° | Estimated Concentration |
| Cinnamyl acetate | 103-54-8 | 0,1 |
| Geraniol | 106-24-1 | 0,05 |
| Methyl eugenol | 93-15-2 | 3 |
| Eugenol | 97-53-0 | 1,1 |
To learn more about IFRA's standards : https://ifrafragrance.org/safe-use/library
ScenTree is solely responsible for the information provided here.


