Clary Sage EO
Naturelle
Herbal > Agrestic > Zesty > Bergamot

Crédits photo: ScenTree SAS
Latin name :
Salvia sclarea
Botanical profile :
Clary sage is a plant of the Lamiaceae family (such as basil, rosemary, mint or patchouli) and of the genus Salvia.
Geographic origin :
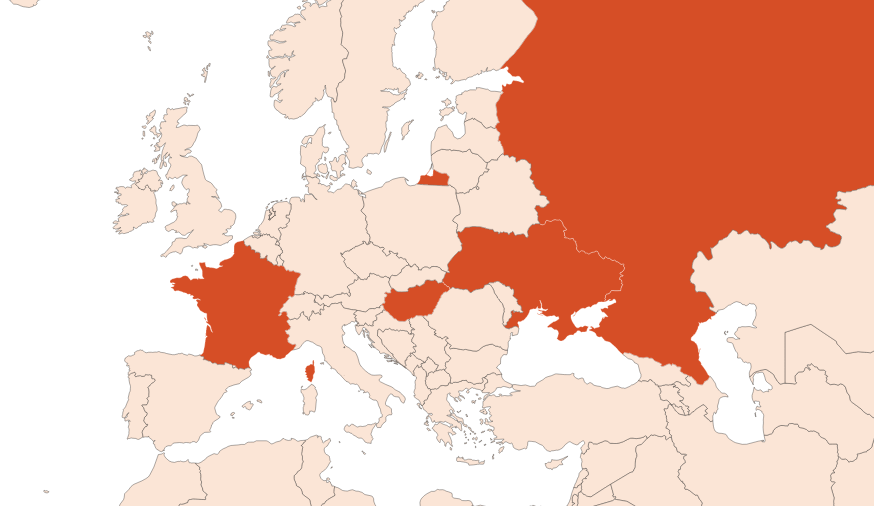
Originally from Western Asia (Middle East and Turkey), clary sage is now mainly grown in France, Russia, the United States and Hungary.
Chemotypes :
The genus Salvia is composed by almost 1000 species, which can be classified according to their composition:
Linalyl Acetate and other esters sages : Clary sage EO / Clary Sage Absolute (Salvia sclaréa - Europe), Doris sage (Salvia dorisiana - rich in Perillyl Acetate) and Sardinian sage (Salvia desoleana - rich in Linalyl Acetate and Terpinyl Acetate).
Eucalyptol or Camphor sages : Including the Lavender-leaved sage (Salvia lavandulifolia), the Three-lobed sage (Salvia fruticosa), the Bengal sage (Salvia bengalensis - India and Pakistan), the White sage (Salvia apiana - California) and the Dandelion leaved sage from the Atlas (Salvia ancheri).
Thujones sage : Including the Dalmatian Sage EO (Salvia officinalis) and all its varieties. Apple sage (Salvia pomifera from Crete, with Beta-Thujone).
Bisabolol or Nerolidol sages : Including the two chemotypes of the blue mountains sages of South Africa (Salvia stenophylla).
Beta-Caryophyllene and other sesquiterpenes sages : Such as the Spanish sage (Salvia hispanica - Beta-Caryophyllene), the Glutinous sage (Salvia glutinosa - γ-Muurolene), the Gentian sage (Salvia tomentosa - Beta-Caryophyllene and Borneol) and the Pineapple sage (Salvia elegans - Central America, with Beta-Caryophyllene and trans-β-Ocimene).
Diterpenoids sages : Such as the Chinese sage (Salvia miltiorrhiza), whose roots are extracted for their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
Linalyl Acetate and other esters sages : Clary sage EO / Clary Sage Absolute (Salvia sclaréa - Europe), Doris sage (Salvia dorisiana - rich in Perillyl Acetate) and Sardinian sage (Salvia desoleana - rich in Linalyl Acetate and Terpinyl Acetate).
Eucalyptol or Camphor sages : Including the Lavender-leaved sage (Salvia lavandulifolia), the Three-lobed sage (Salvia fruticosa), the Bengal sage (Salvia bengalensis - India and Pakistan), the White sage (Salvia apiana - California) and the Dandelion leaved sage from the Atlas (Salvia ancheri).
Thujones sage : Including the Dalmatian Sage EO (Salvia officinalis) and all its varieties. Apple sage (Salvia pomifera from Crete, with Beta-Thujone).
Bisabolol or Nerolidol sages : Including the two chemotypes of the blue mountains sages of South Africa (Salvia stenophylla).
Beta-Caryophyllene and other sesquiterpenes sages : Such as the Spanish sage (Salvia hispanica - Beta-Caryophyllene), the Glutinous sage (Salvia glutinosa - γ-Muurolene), the Gentian sage (Salvia tomentosa - Beta-Caryophyllene and Borneol) and the Pineapple sage (Salvia elegans - Central America, with Beta-Caryophyllene and trans-β-Ocimene).
Diterpenoids sages : Such as the Chinese sage (Salvia miltiorrhiza), whose roots are extracted for their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
Extraction process :
Clary sage is a short-lived plant, measuring up to 1.60 m in cultivation. In early spring, the clary sage fields are perennialized by sowing the seeds of the plant. Harvesting takes place during the flowering period in August. The harvest is mechanical: a tractor cuts, shreds and recovers the fresh plants before taking them to the extraction factory.
The leaves can be extracted fresh or dry. The process then used depends on the efficiency and yield with which the essential oil is wanted to be obtained. The extraction is carried out by steam entrainment for one or two hours under high water vapour pressure. The essential oil is recovered from the refrigerant outlet by settling over the clary sage hydrolate. If this extraction is carried out on the fresh product, the yield is 0.1%. If it is carried out on dry leaves, the yield is 0.2%.
A clary sage absolute can also be obtained by extraction with volatile solvents. The resulting extract has a much more coumarinous, Hay Absolute and slightly spicy smell.
The leaves can be extracted fresh or dry. The process then used depends on the efficiency and yield with which the essential oil is wanted to be obtained. The extraction is carried out by steam entrainment for one or two hours under high water vapour pressure. The essential oil is recovered from the refrigerant outlet by settling over the clary sage hydrolate. If this extraction is carried out on the fresh product, the yield is 0.1%. If it is carried out on dry leaves, the yield is 0.2%.
A clary sage absolute can also be obtained by extraction with volatile solvents. The resulting extract has a much more coumarinous, Hay Absolute and slightly spicy smell.
Major Components :
Linalyl Acetate (50-60%)
Linalool (20-30%)
Alpha-Terpineol (5-10%)
Gamma-Caryophyllene (≈3%)
Geraniol (≈1%)
Linalool (20-30%)
Alpha-Terpineol (5-10%)
Gamma-Caryophyllene (≈3%)
Geraniol (≈1%)
- Uses in perfumery :
- Used in lavender, lavandin and bergamot accords to give a natural effect. Clary sage essential oil is used more than absolute because it is more effective and profitable, due to its heady note and price.
- Other comments :
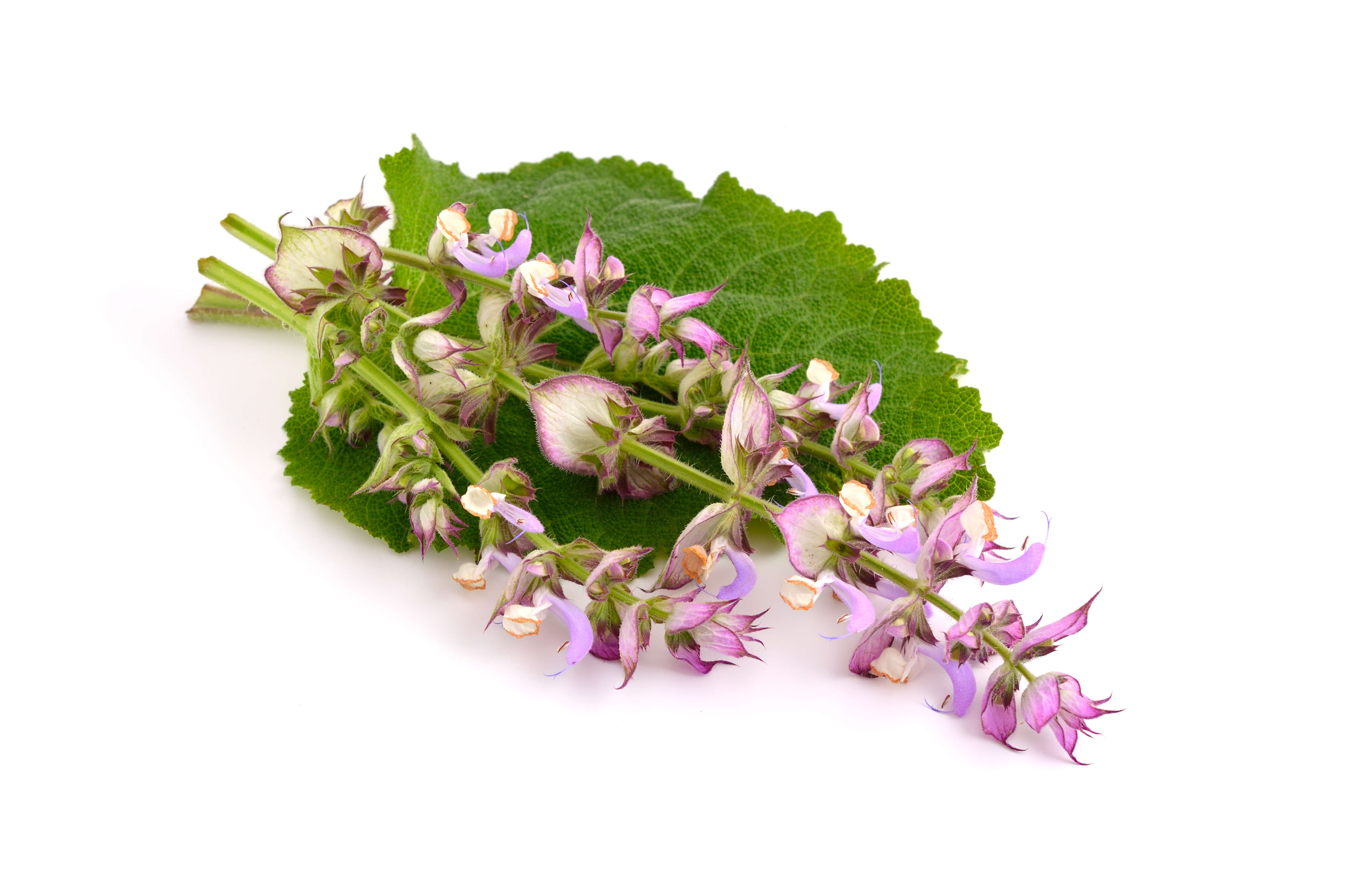
- Clary sage comes in the form of long leafy stems with purple-blue floral buds. The leaves contain the essential oil.
Clary sage essential oil can be a precursor of natural Linalyl Acetate, its main component. However, Bergamot EO is often preferred to extract it at a lower cost. - Volatility :
- Head/Heart
- Appearance :
- Pale green liquid
- Stability :
- Esters of this essential may form their corresponding acids in stability.
Also, terpenes found in this essential oil can polymerize under the effect of oxydation. - Price Range :
- €€
- Aromatherapy :
Informations provided below are taken from reference works in aromatherapy. They are given for information purposes only and can not constitute medical information, nor engage the responsibility of ScenTree.
Clary sage extracts are recommended for use in menopausal disorders.
Crédits photo: ScenTree SAS
- EINECS number :
- 84775-83-7
- FEMA number :
- 2321
- Allergens :
- Linalool - Geraniol - D-Limonene
- IFRA :
- This ingredient is restricted by IFRA
- Annexe I :
- Some regulated synthetic ingredients are found in nature and in certain proportions in natural ingredients. This presence in nature has to be taken into account when calculating limits of use recommended by the IFRA. In case you do not know these concentrations, you can use the ones estimated by the IFRA. Here they are :
- Annexe I :
- Some regulated synthetic ingredients are found in nature and in certain proportions in natural ingredients. This presence in nature has to be taken into account when calculating limits of use recommended by the IFRA. In case you do not know these concentrations, you can use the ones estimated by the IFRA. Here they are :
| List of regulated compounds contained in this ingredient | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regulated ingredient name | CAS N° | Estimated Concentration |
| Geraniol | 106-24-1 | 1,2 |
| List of regulated compounds contained in this ingredient | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regulated ingredient name | CAS N° | Estimated Concentration |
| Geraniol | 106-24-1 | 1,2 |
To learn more about IFRA's standards : https://ifrafragrance.org/safe-use/library
ScenTree is solely responsible for the information provided here.




