Ho Wood EO
Naturelle
Floral > Fresh Flowers > Lavender > Zesty

Crédits photo: ScenTree SAS
Latin name :
Cinnamomum camphora var. linaloolifera
Botanical profile :
Ho Wood is a tree belonging to the Lauraceae family and the Cinnamomum genus.
Geographic origin :
Originally from China, Taiwan and Japan, ho wood has spread to other continents, but remains mainly cultivated in its countries of origin.
Chemotypes :
Ho wood is a variety of camphor tree. The variety we are talking about here is called Cinnamomum camphora var. linaloolifera. This variety is not used to extract camphor, unlike the classic camphor tree. Its essential oil is made up of a large amount of Linalool.
The Cinnamomum genus includes more than 250 species throughout Asia. It includes all varieties of cinnamon tree, of which Cinnamomum zeylanicum (Ceylon Cinnamon EO) and Cinnamomum cassia (Chinese Cinnamon EO) are the most commonly used in perfumery, for their bark and for their leaves (Cinnamon Leaf EO).
The Cinnamomum genus includes more than 250 species throughout Asia. It includes all varieties of cinnamon tree, of which Cinnamomum zeylanicum (Ceylon Cinnamon EO) and Cinnamomum cassia (Chinese Cinnamon EO) are the most commonly used in perfumery, for their bark and for their leaves (Cinnamon Leaf EO).
Extraction process :
Ho wood is a tree that can measure up to 25 meters high, with green leaves alternating along the branches.
In perfumery, the wood is most often extracted, even if the leaves are also very fragrant. An indication of tree maturity is the colour of its leaves: the tree can be cultivated when its leaves turn from red to green.
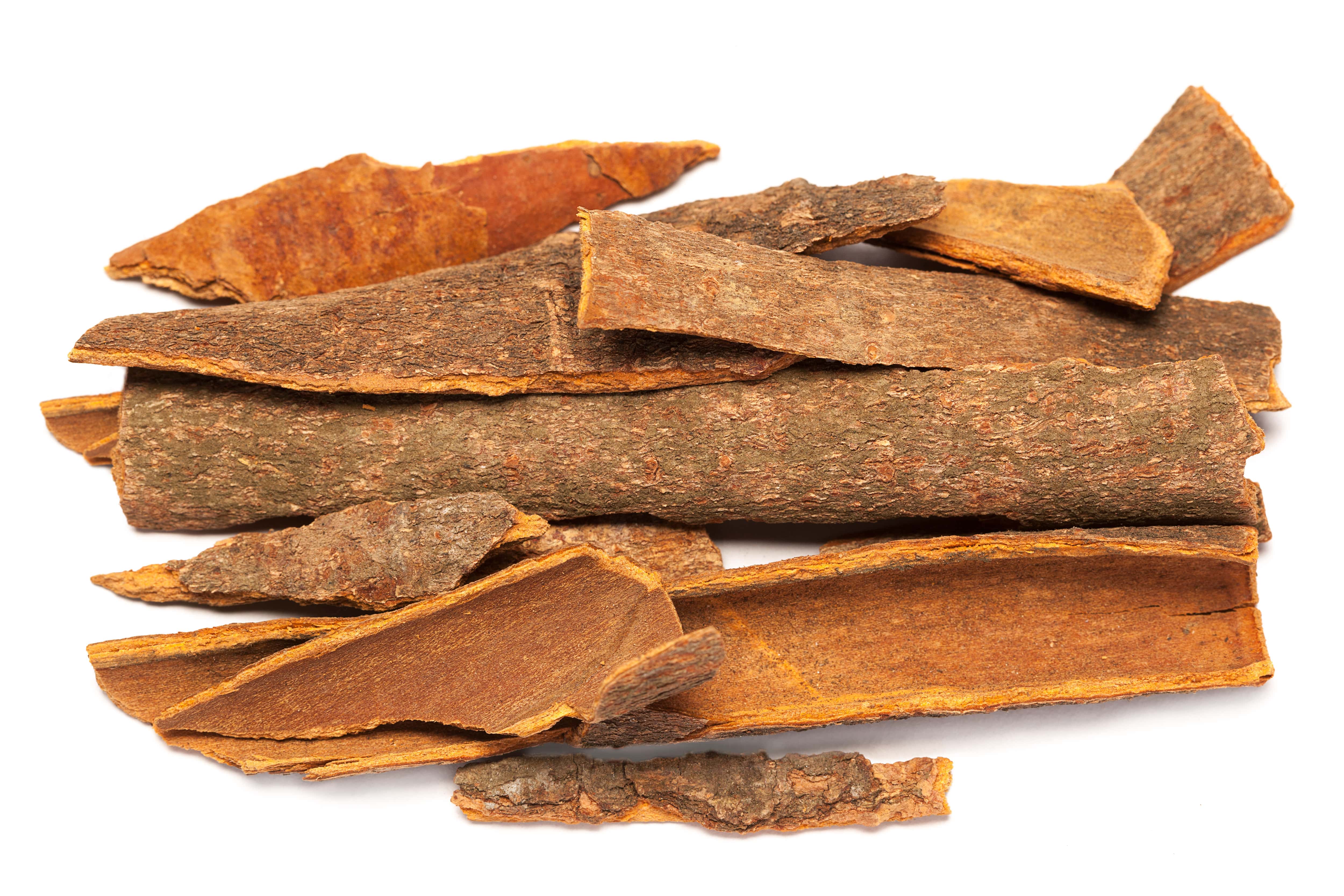
The bark of this wood is separated by cutting it into strips, from the surface towards the centre of the trunk. After uncoupling from the trunk, the pieces of bark are dried to develop their olfactory potential. It is then that ho wood can be extracted by steam distillation. Extraction is carried out on the bark strips as they are or slightly crushed. The essential oil is recovered after distillation in a Florentine flask, with a yield of 2 to 3%.
The essential oil from the leaves of this tree can also be extracted, and is full of Linalool. The two essential oils of this tree are often rectified to obtain natural Linalool. Ho wood and Rosewood EO are the two main sources of natural Linalool.
In perfumery, the wood is most often extracted, even if the leaves are also very fragrant. An indication of tree maturity is the colour of its leaves: the tree can be cultivated when its leaves turn from red to green.
The bark of this wood is separated by cutting it into strips, from the surface towards the centre of the trunk. After uncoupling from the trunk, the pieces of bark are dried to develop their olfactory potential. It is then that ho wood can be extracted by steam distillation. Extraction is carried out on the bark strips as they are or slightly crushed. The essential oil is recovered after distillation in a Florentine flask, with a yield of 2 to 3%.
The essential oil from the leaves of this tree can also be extracted, and is full of Linalool. The two essential oils of this tree are often rectified to obtain natural Linalool. Ho wood and Rosewood EO are the two main sources of natural Linalool.
Major Components :
Linalool (75-98%)
Linalol Oxide (≈2%)
Linalol Oxide (≈2%)
- Uses in perfumery :
- Ho Wood EO can be used in aromatic notes, to give them a floral nuance and a clean and fresh note. Also used in men's cosmetics, always for a clean facet.
- Other comments :
- Ho wood is a variety of camphor tree. This tree can be used to extract Camphor in its natural state. In perfumery, a chemotype containing Linalool is used (cinnamomum camphora l. linaloolifera). This chemotype, also called Shiu wood, contains almost no Camphor and can be used to extract natural Linalool, such as Rosewood EO for example.
- Volatility :
- Head/Heart
- Appearance :
- Colorless to pale yellow liquid
- Stability :
- Linalool in this essential oil tends to polymerize under the effect of a strong oxydation.
- Price Range :
- €€€
- Aromatherapy :
Informations provided below are taken from reference works in aromatherapy. They are given for information purposes only and can not constitute medical information, nor engage the responsibility of ScenTree.
Ho wood is known for its anti-infective and antifungal properties, and is indicated in case of ENT infection, especially for children.
Crédits photo: ScenTree SAS
- EINECS number :
- 91745-89-0
- FEMA number :
- Donnée indisponible.
- Allergens :
- Linalool
- IFRA :
- This ingredient is restricted by IFRA
- Annexe I :
- Some regulated synthetic ingredients are found in nature and in certain proportions in natural ingredients. This presence in nature has to be taken into account when calculating limits of use recommended by the IFRA. In case you do not know these concentrations, you can use the ones estimated by the IFRA. Here they are :
- Annexe I :
- Some regulated synthetic ingredients are found in nature and in certain proportions in natural ingredients. This presence in nature has to be taken into account when calculating limits of use recommended by the IFRA. In case you do not know these concentrations, you can use the ones estimated by the IFRA. Here they are :
| List of regulated compounds contained in this ingredient | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regulated ingredient name | CAS N° | Estimated Concentration |
| Geraniol | 106-24-1 | 0,4 |
| List of regulated compounds contained in this ingredient | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regulated ingredient name | CAS N° | Estimated Concentration |
| Geraniol | 106-24-1 | 0,4 |
To learn more about IFRA's standards : https://ifrafragrance.org/safe-use/library
ScenTree is solely responsible for the information provided here.


