Styrax EO
Naturelle
Balsamic Ambery > Balsamic > Leather > Plastic > White Flowers

Crédits photo: ScenTree SAS
Latin name :
Liquidambar orientalis
Botanical profile :
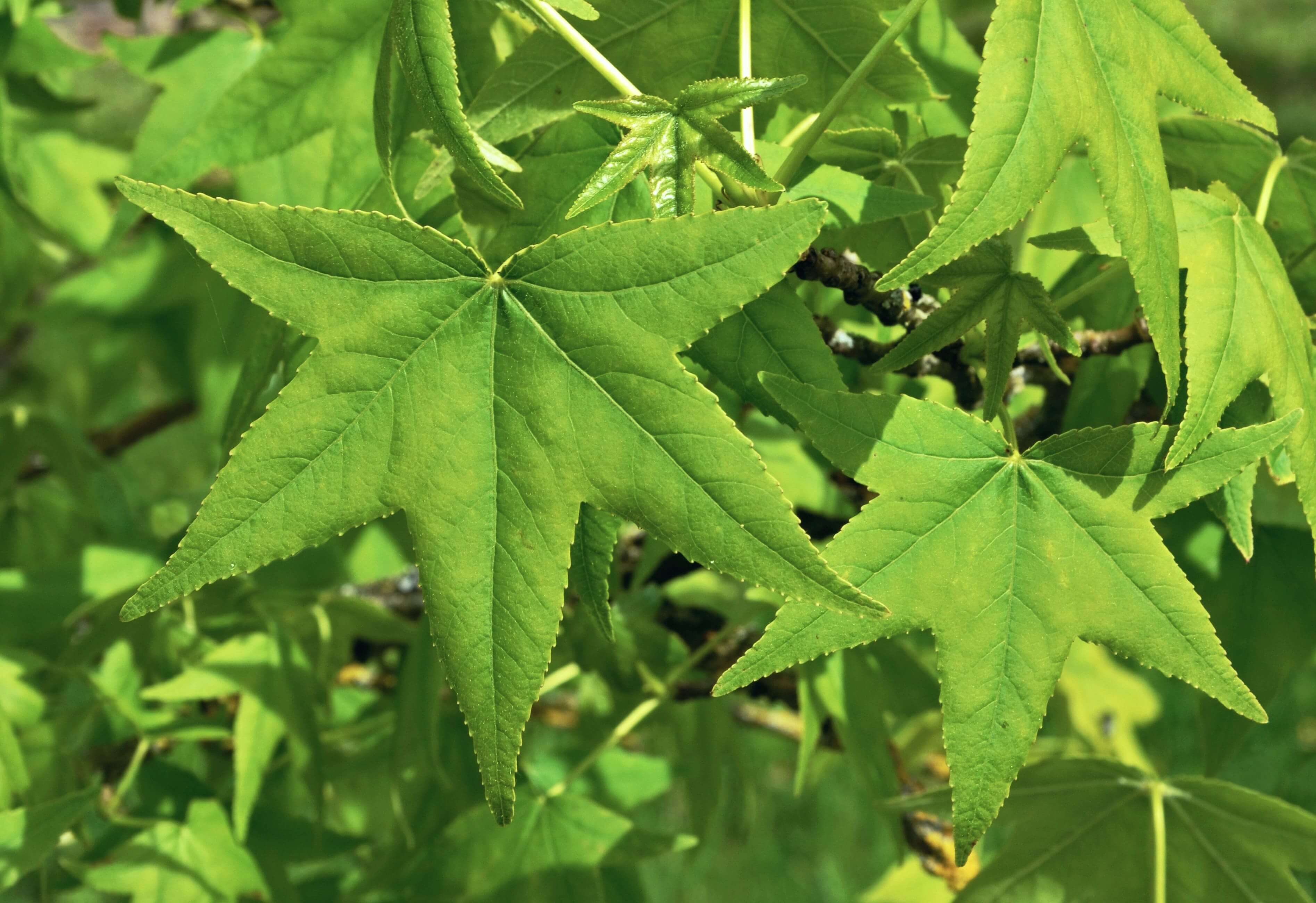
Styrax is a tree of the Hammamelidae family and the genus Liquidambar.
Geographic origin :
Native to Asia Minor, styrax is a tree now grown in Turkey and Central America (particularly in Honduras)
Chemotypes :
The genus Liquidambar has two major species cultivated for perfumery:
The Liquidambar styraciflua (present in Latin America, especially in Honduras) naturally exudes the resin. Its composition is richer in Beta-Caryophyllene.
The Liquidambar orientalis (present in Turkey) must be hammered to exude the resin.
Two other species can be used in perfumery, but on a smaller scale:
The Liquidambar formosana, or Formosan sweetgum, from China.
The Liquidambar acalycina, also from China (South of the country).
The Liquidambar styraciflua (present in Latin America, especially in Honduras) naturally exudes the resin. Its composition is richer in Beta-Caryophyllene.
The Liquidambar orientalis (present in Turkey) must be hammered to exude the resin.
Two other species can be used in perfumery, but on a smaller scale:
The Liquidambar formosana, or Formosan sweetgum, from China.
The Liquidambar acalycina, also from China (South of the country).
Extraction process :
Styrax is a medium-sized tree that secretes a resin in its sapwood (the youngest part of a tree) and its bark.
The resin is naturally secreted by the trees but its secretion can be accelerated by an incision or voluntary hammering of the tree. After a month drying on the tree, the resin is collected to be extracted by steam distillation after filtration.
The drying hardens the resin, which turns brown due to oxidation. Once placed in the distillation tank, the steam distillation is done under pressure and the essential oil is collected at the end of the process, by decantation, with a rather high yield.
Styrax resinoid results from an extraction with alcohol and has more hold, is more ambered, balsamic and warm than the essential oil. There is also a CO2 extract of Styrax, which gives the extract a higher olfactory quality, but is more expensive.
The leaves of the tree can also be extracted, to obtain an essential oil whose composition is more volatile and smell is very terpenic.
The resin is naturally secreted by the trees but its secretion can be accelerated by an incision or voluntary hammering of the tree. After a month drying on the tree, the resin is collected to be extracted by steam distillation after filtration.
The drying hardens the resin, which turns brown due to oxidation. Once placed in the distillation tank, the steam distillation is done under pressure and the essential oil is collected at the end of the process, by decantation, with a rather high yield.
Styrax resinoid results from an extraction with alcohol and has more hold, is more ambered, balsamic and warm than the essential oil. There is also a CO2 extract of Styrax, which gives the extract a higher olfactory quality, but is more expensive.
The leaves of the tree can also be extracted, to obtain an essential oil whose composition is more volatile and smell is very terpenic.
Major Components :
Styrene (≈70%)
Alpha-Pinene (≈20%)
Beta-Pinene (≈4%)
Benzyl Cinnamate (≈2%)
Cinnamyl Alcohol (≈2%)
D-Limonene (≈1%)
Camphene (≈1%)
Alpha-Pinene (≈20%)
Beta-Pinene (≈4%)
Benzyl Cinnamate (≈2%)
Cinnamyl Alcohol (≈2%)
D-Limonene (≈1%)
Camphene (≈1%)
- Uses in perfumery :
- Used in fine fragrance for floral-hyacinth, tuberose, rose, carnation notes. Useful in amber, leather, chypre and spicy notes.
- Other comments :
- The fragrant ambered resin secreted by the tree is intended to heal the bark in case of incision or natural injury. In ancient Egypt, Styrax was used for fumigations as an offering to the gods, as well as myrrh and khyphi.
Styrax is sometimes called storax, as it was in the old days.
Globally, Styrax EO Pyrogenated is used to bring a smoky woods aspect to leather compositions, Styrax EO for its white flowers facet and Styrax Resinoid for an animalic note. - Volatility :
- Heart
- Appearance :
- Viscous amber liquid
- Stability :
- Solubility issues in perfumes
Aromatic compounds can be chromophoric and cause a coloration of the oil, especially in alkaline bases - Price Range :
- €€€€
- Aromatherapy :
Informations provided below are taken from reference works in aromatherapy. They are given for information purposes only and can not constitute medical information, nor engage the responsibility of ScenTree.
Styrax resin is known for its antitussive properties (cough) and is therefore recommended for bronchitis.
Crédits photo: ScenTree SAS
- EINECS number :
- 305-627-6
- FEMA number :
- Donnée indisponible.
- Allergens :
- Cinnamyl Alcohol - Cinnamaldehyde - Benzyl Cinnamate
- IFRA :
- This ingredient is restricted by IFRA
- Restriction type :
- PROHIBITION_RESTRICTION_SPECIFICATION
- Cause of restriction :
- DERMAL SENSITIZATION
- Amendment :
- 49
- Comments :
- Crude gums of Liquidambar styraficula L. var. macrophylla or Liquidambar orientalis Mill. should not be used as fragrance ingredients for any finished product application. Only extracts or distillates (resinoids, absolutes and oils), prepared from exudations of Liquidambar styraciflua L. var. macrophylla or Liquidambar orientalis Mill., can be used. Styrax oil can be obtained from solvent extraction or pyrolysis. Styrax oil obtained through pyrolysis shall be rectified according to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and the content of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAH) resulting from their use shall respect the following requirement: Benzopyrene and 1,2-Benzanthracene are to be used as markers for PAH. If used alone or in combination with rectified Cade oil, rectified Birch tar oils or rectified Opoponax oil, the total concentration of both of the markers should not exceed 1 ppb in the final product.
- Quantitative limit on the use :
-
Cat.1 Cat.2 Cat.3 Cat.4 Cat.5A Cat.5B Cat.5C Cat.5D Cat.6 0,12 % 0,034 % 0,69 % 0,64 % 0,16 % 0,16 % 0,16 % 0,16 % 0,38 % Cat.7A Cat.7B Cat.8 Cat.9 Cat.10A Cat.10B Cat.11A Cat.11B Cat.12 1,3 % 1,3 % 0,068 % 1,3 % 4,5 % 4,5 % 2,5 % 2,5 % No Restriction - Annexe I :
- Some regulated synthetic ingredients are found in nature and in certain proportions in natural ingredients. This presence in nature has to be taken into account when calculating limits of use recommended by the IFRA. In case you do not know these concentrations, you can use the ones estimated by the IFRA. Here they are :
- Restriction type :
- RESTRICTION QRA
- Cause of restriction :
- SENSITIZATION
- Amendment :
- 47
- Comments :
- Crude gums of Liquidambar styraficula L. var. macrophylla or Liquidambar orientalis Mill. should not be used as fragrance ingredients: Only extracts or distillates (resinoids, absolutes and oils), prepared from exudations of Liquidambar styraciflua L. var. macrophylla or Liquidambar orientalis Mill., can be used.This recommendation is made in order to promote good manufacturing practice (GMP) for the use of styrax derivatives as fragrance ingredients. It is based on a wide variety of RIFM test data with gums, resinoids, absolutes and oils of American and Asian styrax (private communication to IFRA). In addition, Styrax oil can be obtained from solvent extraction or pyrolysis. Styrax oil obtained through pyrolysis shall be rectified according to Good Manufacturing Practices and the content of polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) resulting from their use shall respect the following requirement: Benzopyrene and 1,2-Benzanthracene are to be used as markers for PAH. If used alone or in combination with rectified Cade oil, rectified Birch tar oils or rectified Opoponax oil, the total concentration of both of the markers should not exceed 1 ppb in the final product.
- Quantitative usage limits :
-
Cat.1 Cat.2 Cat.3 Cat.4 Cat.5 Cat.6 Cat.7 Cat.8 Cat.9 Cat.10 Cat.11 0,04 % 0,05 % 0,23 % 0,6 % 0,36 % 0,6 % 0,11 % 0,6 % 0,6 % 0,6 % Not Restricted - Annexe I :
- Some regulated synthetic ingredients are found in nature and in certain proportions in natural ingredients. This presence in nature has to be taken into account when calculating limits of use recommended by the IFRA. In case you do not know these concentrations, you can use the ones estimated by the IFRA. Here they are :
| List of regulated compounds contained in this ingredient | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regulated ingredient name | CAS N° | Estimated Concentration |
| Benzaldehyde | 100-52-7 | 0,1 |
| Benzyl cinnamate | 103-41-3 | 2,1 |
| Cinnamic alcohol | 104-54-1 | 1,5 |
| Cinnamic aldehyde | 104-55-2 | 0,1 |
| List of regulated compounds contained in this ingredient | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regulated ingredient name | CAS N° | Estimated Concentration |
| Benzaldehyde | 100-52-7 | 0,1 |
| Benzyl cinnamate | 103-41-3 | 2,1 |
| Cinnamic alcohol | 104-54-1 | 1,5 |
| Cinnamic aldehyde | 104-55-2 | 0,1 |
To learn more about IFRA's standards : https://ifrafragrance.org/safe-use/library
ScenTree is solely responsible for the information provided here.


